Page 251 - Clinical Manual of Small Animal Endosurgery
P. 251
Upper Respiratory Tract 239
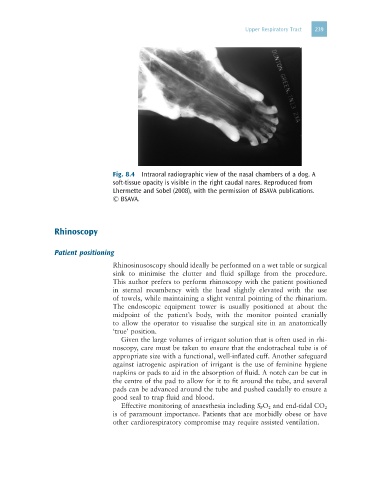
Fig. 8.4 Intraoral radiographic view of the nasal chambers of a dog. A
soft-tissue opacity is visible in the right caudal nares. Reproduced from
Lhermette and Sobel (2008), with the permission of BSAVA publications.
© BSAVA.
Rhinoscopy
Patient positioning
Rhinosinusoscopy should ideally be performed on a wet table or surgical
sink to minimise the clutter and fluid spillage from the procedure.
This author prefers to perform rhinoscopy with the patient positioned
in sternal recumbency with the head slightly elevated with the use
of towels, while maintaining a slight ventral pointing of the rhinarium.
The endoscopic equipment tower is usually positioned at about the
midpoint of the patient’s body, with the monitor pointed cranially
to allow the operator to visualise the surgical site in an anatomically
‘true’ position.
Given the large volumes of irrigant solution that is often used in rhi-
noscopy, care must be taken to ensure that the endotracheal tube is of
appropriate size with a functional, well-inflated cuff. Another safeguard
against iatrogenic aspiration of irrigant is the use of feminine hygiene
napkins or pads to aid in the absorption of fluid. A notch can be cut in
the centre of the pad to allow for it to fit around the tube, and several
pads can be advanced around the tube and pushed caudally to ensure a
good seal to trap fluid and blood.
Effective monitoring of anaesthesia including S P O 2 and end-tidal CO 2
is of paramount importance. Patients that are morbidly obese or have
other cardiorespiratory compromise may require assisted ventilation.