Page 150 - Fluid, Electrolyte, and Acid-Base Disorders in Small Animal Practice
P. 150
140 ELECTROLYTE DISORDERS
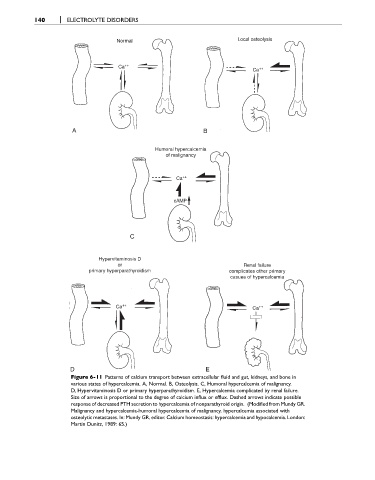
Normal Local osteolysis
Ca ++ ++
Ca
A B
Humoral hypercalcemia
of malignancy
Ca ++
cAMP
C
Hypervitaminosis D
or Renal failure
primary hyperparathyroidism complicates other primary
casues of hypercalcemia
Ca ++ Ca ++
D E
Figure 6-11 Patterns of calcium transport between extracellular fluid and gut, kidneys, and bone in
various states of hypercalcemia. A, Normal. B, Osteolysis. C, Humoral hypercalcemia of malignancy.
D, Hypervitaminosis D or primary hyperparathyroidism. E, Hypercalcemia complicated by renal failure.
Size of arrows is proportional to the degree of calcium influx or efflux. Dashed arrows indicate possible
response of decreased PTH secretion to hypercalcemia of nonparathyroid origin. (Modified from Mundy GR.
Malignancy and hypercalcemia-humoral hypercalcemia of malignancy, hypercalcemia associated with
osteolytic metastases. In: Mundy GR, editor. Calcium homeostasis: hypercalcemia and hypocalcemia. London:
Martin Dunitz, 1989: 65.)