Page 170 - Withrow and MacEwen's Small Animal Clinical Oncology, 6th Edition
P. 170
CHAPTER 8 Molecular Diagnostics 149
100 110 120 130 140 150 160 170 180 190 200 210 220 230 240
VetBooks.ir 12,000
10,000
8,000
6,000
4,000
2,000
Exons 1–7 8 9–10 11 12–21
0
Exons 1–7 8 9–10 11 12–21
132.5
100 110 120 130 140 150 160 170 180 190 200 210 220 230 240
Exons 1–7 8 9–10 11 12–21
9,000
8,000
Exons 1–7 8 9–10 11 12–21
7,000
6,000
5,000
4,000
3,000
2,000
1,000
0
1,000
A 132.6
85 90 95 100 105 110 115 120 125 130 135 140 145
18,000
16,000
14,000
12,000
10,000
8,000
6,000
4,000
Exons 1–7 8 9–10 11 12–21 2,000
0
Exons 1–7 8 9–10 11 12–21 2,000
91.9
85 90 95 100 105 110 115 120 125 130 135 140 145
Exons 1–7 8 9–10 11 12–21
16,000
Exons 1–7 8 9–10 11 12–21 14,000
12,000
10,000
8,000
6,000
4,000
2,000
0
B 91.8
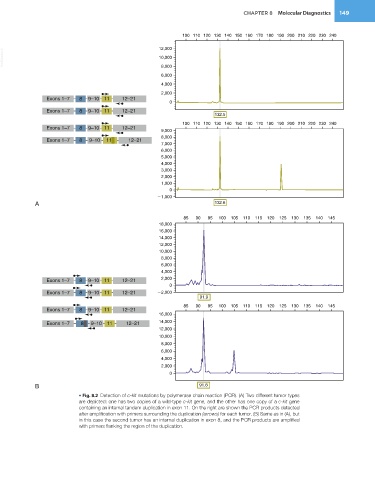
• Fig. 8.2 Detection of c-kit mutations by polymerase chain reaction (PCR). (A) Two different tumor types
are depicted: one has two copies of a wild-type c-kit gene, and the other has one copy of a c-kit gene
containing an internal tandem duplication in exon 11. On the right are shown the PCR products detected
after amplification with primers surrounding the duplication (arrows) for each tumor. (B) Same as in (A), but
in this case the second tumor has an internal duplication in exon 8, and the PCR products are amplified
with primers flanking the region of the duplication.