Page 173 - Withrow and MacEwen's Small Animal Clinical Oncology, 6th Edition
P. 173
152 PART II Diagnostic Procedures for the Cancer Patient
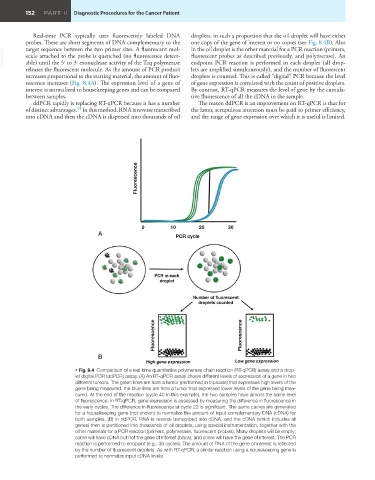
Real-time PCR typically uses fluorescently labeled DNA droplets, in such a proportion that the oil droplet will have either
probes. These are short segments of DNA complementary to the one copy of the gene of interest or no copies (see Fig. 8.4B). Also
in the oil droplet is the other material for a PCR reaction (primers,
target sequence between the two primer sites. A fluorescent mol-
VetBooks.ir ecule attached to the probe is quenched (no fluorescence detect- fluorescent probes as described previously, and polymerase). An
endpoint PCR reaction is performed in each droplet (all drop-
able) until the 5′ to 3′ exonuclease activity of the Taq polymerase
releases the fluorescent molecule. As the amount of PCR product lets are amplified simultaneously), and the number of fluorescent
increases proportional to the starting material, the amount of fluo- droplets is counted. This is called “digital” PCR because the level
rescence increases (Fig. 8.4A). The expression level of a gene of of gene expression is correlated with the count of positive droplets.
interest is normalized to housekeeping genes and can be compared By contrast, RT-qPCR measures the level of gene by the cumula-
between samples. tive fluorescence of all the cDNA in the sample.
ddPCR rapidly is replacing RT-qPCR because it has a number The reason ddPCR is an improvement on RT-qPCR is that for
of distinct advantages. In this method, RNA is reverse transcribed the latter, scrupulous attention must be paid to primer efficiency,
43
into cDNA and then the cDNA is dispersed into thousands of oil and the range of gene expression over which it is useful is limited.
Fluorescence
0 10 20 30
A PCR cycle
PCR in each
droplet
Number of fluorescent
droplets counted
Fluorescence Fluorescence
B
High gene expression Low gene expression
• Fig. 8.4 Comparison of a real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR) assay and a drop-
let digital PCR (ddPCR) assay. (A) An RT-qPCR assay shows different levels of expression of a gene in two
different tumors. The green lines are from a tumor (performed in triplicate) that expresses high levels of the
gene being measured; the blue lines are from a tumor that expresses lower levels of the gene being mea-
sured. At the end of the reaction (cycle 40 in this example), the two samples have almost the same level
of fluorescence. In RT-qPCR, gene expression is assessed by measuring the difference in fluorescence in
the early cycles. The difference in fluorescence at cycle 22 is significant. The same curves are generated
for a housekeeping gene (not shown) to normalize the amount of input complementary DNA (cDNA) for
both samples. (B) In ddPCR, RNA is reverse transcribed into cDNA, and the cDNA (which includes all
genes) then is partitioned into thousands of oil droplets, using special instrumentation, together with the
other materials for a PCR reaction (primers, polymerase, fluorescent probes). Many droplets will be empty;
some will have cDNA but not the gene of interest (black); and some will have the gene of interest. The PCR
reaction is performed to endpoint (e.g., 30 cycles). The amount of RNA of the gene of interest is reflected
by the number of fluorescent droplets. As with RT-qPCR, a similar reaction using a housekeeping gene is
performed to normalize input cDNA levels.