Page 396 - Withrow and MacEwen's Small Animal Clinical Oncology, 6th Edition
P. 396
374 PART IV Specific Malignancies in the Small Animal Patient
VetBooks.ir
A B
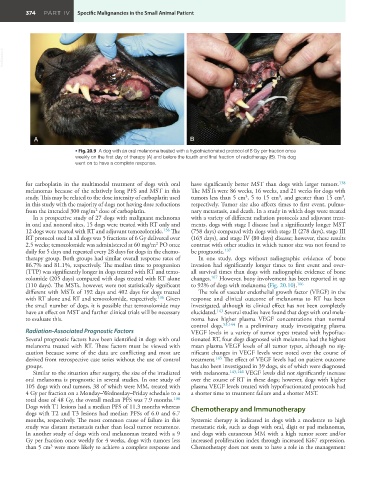
• Fig. 20.9 A dog with an oral melanoma treated with a hypofractionated protocol of 8 Gy per fraction once
weekly on the first day of therapy (A) and before the fourth and final fraction of radiotherapy (B). This dog
went on to have a complete response.
for carboplatin in the multimodal treatment of dogs with oral have significantly better MST than dogs with larger tumors. 138
melanomas because of the relatively long PFS and MST in this The MSTs were 86 weeks, 16 weeks, and 21 weeks for dogs with
3
study. This may be related to the dose intensity of carboplatin used tumors less than 5 cm , 5 to 15 cm , and greater than 15 cm ,
3
3
in this study with the majority of dogs not having dose reductions respectively. Tumor size also affects times to first event, pulmo-
from the intended 300 mg/m dose of carboplatin. nary metastasis, and death. In a study in which dogs were treated
2
In a prospective study of 27 dogs with malignant melanoma with a variety of different radiation protocols and adjuvant treat-
in oral and nonoral sites, 15 dogs were treated with RT only and ments, dogs with stage I disease had a significantly longer MST
12 dogs were treated with RT and adjuvant temozolomide. 136 The (758 days) compared with dogs with stage II (278 days), stage III
RT protocol used in all dogs was 5 fractions of 6 Gy delivered over (163 days), and stage IV (80 days) disease; however, these results
2.5 weeks; temozolomide was administered at 60 mg/m PO once contrast with other studies in which tumor size was not found to
2
daily for 5 days and repeated every 28 days for dogs in the chemo- be prognostic. 137
therapy group. Both groups had similar overall response rates of In one study, dogs without radiographic evidence of bone
86.7% and 81.1%, respectively. The median time to progression invasion had significantly longer times to first event and over-
(TTP) was significantly longer in dogs treated with RT and temo- all survival times than dogs with radiographic evidence of bone
zolomide (205 days) compared with dogs treated with RT alone changes. 107 However, bony involvement has been reported in up
(110 days). The MSTs, however, were not statistically significant to 92% of dogs with melanoma (Fig. 20.10). 106
different with MSTs of 192 days and 402 days for dogs treated The role of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) in the
with RT alone and RT and temozolomide, respectively. 136 Given response and clinical outcome of melanomas to RT has been
the small number of dogs, it is possible that temozolomide may investigated, although its clinical effect has not been completely
have an effect on MST and further clinical trials will be necessary elucidated. 143 Several studies have found that dogs with oral mela-
to evaluate this. noma have higher plasma VEGF concentrations than normal
control dogs. 53,144 In a preliminary study investigating plasma
Radiation-Associated Prognostic Factors VEGF levels in a variety of tumor types treated with hypofrac-
Several prognostic factors have been identified in dogs with oral tionated RT, four dogs diagnosed with melanoma had the highest
melanoma treated with RT. These factors must be viewed with mean plasma VEGF levels of all tumor types, although no sig-
caution because some of the data are conflicting and most are nificant changes in VEGF levels were noted over the course of
derived from retrospective case series without the use of control treatment. 145 The effect of VEGF levels had on patient outcome
groups. has also been investigated in 39 dogs, six of which were diagnosed
Similar to the situation after surgery, the size of the irradiated with melanoma. 145,146 VEGF levels did not significantly increase
oral melanoma is prognostic in several studies. In one study of over the course of RT in these dogs; however, dogs with higher
105 dogs with oral tumors, 38 of which were MM, treated with plasma VEGF levels treated with hypofractionated protocols had
4 Gy per fraction on a Monday–Wednesday–Friday schedule to a a shorter time to treatment failure and a shorter MST.
total dose of 48 Gy, the overall median PFS was 7.9 months. 108
Dogs with T1 lesions had a median PFS of 11.3 months whereas Chemotherapy and Immunotherapy
dogs with T2 and T3 lesions had median PFSs of 6.0 and 6.7
months, respectively. The most common cause of failure in this Systemic therapy is indicated in dogs with a moderate to high
study was distant metastasis rather than local tumor recurrence. metastatic risk, such as dogs with oral, digit or pad melanomas,
In another study of dogs with oral melanomas treated with a 9 and dogs with cutaneous MM with a high tumor score and/or
Gy per fraction once weekly for 4 weeks, dogs with tumors less increased proliferation index through increased Ki67 expression.
3
than 5 cm were more likely to achieve a complete response and Chemotherapy does not seem to have a role in the management