Page 563 - Withrow and MacEwen's Small Animal Clinical Oncology, 6th Edition
P. 563
CHAPTER 25 Tumors of the Skeletal System 541
VetBooks.ir
A B
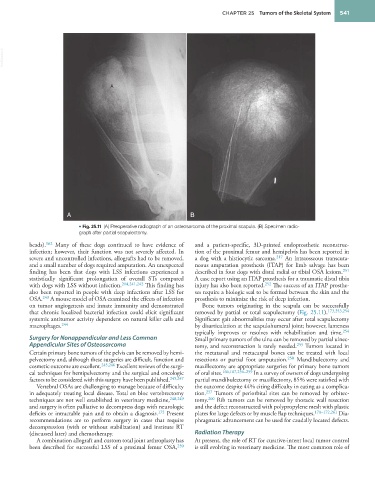
• Fig. 25.11 (A) Preoperative radiograph of an osteosarcoma of the proximal scapula. (B) Specimen radio-
graph after partial scapulectomy.
beads). 162 Many of these dogs continued to have evidence of and a patient-specific, 3D-printed endoprosthetic reconstruc-
infection; however, their function was not severely affected. In tion of the proximal femur and hemipelvis has been reported in
severe and uncontrolled infections, allografts had to be removed, a dog with a histiocytic sarcoma. 217 An intraosseous transcuta-
and a small number of dogs required amputation. An unexpected neous amputation prosthesis (ITAP) for limb salvage has been
finding has been that dogs with LSS infections experienced a described in four dogs with distal radial or tibial OSA lesions. 251
statistically significant prolongation of overall STs compared A case report using an ITAP prosthesis for a traumatic distal tibia
with dogs with LSS without infection. 214,241,242 This finding has injury has also been reported. 252 The success of an ITAP prosthe-
also been reported in people with deep infections after LSS for ses require a biologic seal to be formed between the skin and the
OSA. 243 A mouse model of OSA examined the effects of infection prosthesis to minimize the risk of deep infection.
on tumor angiogenesis and innate immunity and demonstrated Bone tumors originating in the scapula can be successfully
that chronic localized bacterial infection could elicit significant removed by partial or total scapulectomy (Fig. 25.11). 173,253,254
systemic antitumor activity dependent on natural killer cells and Significant gait abnormalities may occur after total scapulectomy
macrophages. 244 by disarticulation at the scapulohumeral joint; however, lameness
typically improves or resolves with rehabilitation and time. 254
Surgery for Nonappendicular and Less Common Small primary tumors of the ulna can be removed by partial ulnec-
Appendicular Sites of Osteosarcoma tomy, and reconstruction is rarely needed. 255 Tumors located in
Certain primary bone tumors of the pelvis can be removed by hemi- the metatarsal and metacarpal bones can be treated with local
pelvectomy and, although these surgeries are difficult, function and resections or partial foot amputation. 250 Mandibulectomy and
cosmetic outcome are excellent. 245,246 Excellent reviews of the surgi- maxillectomy are appropriate surgeries for primary bone tumors
cal techniques for hemipelvectomy and the surgical and oncologic of oral sites. 166,167,256–259 In a survey of owners of dogs undergoing
factors to be considered with this surgery have been published. 245,247 partial mandibulectomy or maxillectomy, 85% were satisfied with
Vertebral OSAs are challenging to manage because of difficulty the outcome despite 44% citing difficulty in eating as a complica-
in adequately treating local disease. Total en bloc vertebrectomy tion. 257 Tumors of periorbital sites can be removed by orbitec-
techniques are not well established in veterinary medicine, 248,249 tomy. 260 Rib tumors can be removed by thoracic wall resection
and surgery is often palliative to decompress dogs with neurologic and the defect reconstructed with polypropylene mesh with plastic
deficits or intractable pain and to obtain a diagnosis. 175 Present plates for large defects or by muscle flap techniques. 170–172,261 Dia-
recommendations are to perform surgery in cases that require phragmatic advancement can be used for caudally located defects.
decompression (with or without stabilization) and institute RT
(discussed later) and chemotherapy. Radiation Therapy
A combination allograft and custom total joint arthroplasty has At present, the role of RT for curative-intent local tumor control
been described for successful LSS of a proximal femur OSA, 250 is still evolving in veterinary medicine. The most common role of