Page 275 - Veterinary Histology of Domestic Mammals and Birds, 5th Edition
P. 275
Respiratory system (apparatus respiratorius) 257
VetBooks.ir
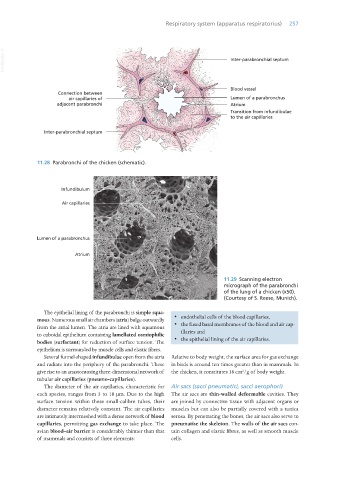
11.28 Parabronchi of the chicken (schematic).
11.29 Scanning electron
micrograph of the parabronchi
of the lung of a chicken (x50).
(Courtesy of S. Reese, Munich).
The epithelial lining of the parabronchi is simple squa-
mous. Numerous small air chambers (atria) bulge outwardly · endothelial cells of the blood capillaries,
from the atrial lumen. The atria are lined with squamous · the fused basal membranes of the blood and air cap-
to cuboidal epithelium containing lamellated osmiophilic illaries and
bodies (surfactant) for reduction of surface tension. The · the epithelial lining of the air capillaries.
epithelium is surrounded by muscle cells and elastic fibres.
Several funnel-shaped infundibulae open from the atria Relative to body weight, the surface area for gas exchange
and radiate into the periphery of the parabronchi. These in birds is around ten times greater than in mammals. In
2
give rise to an anastomosing three-dimensional network of the chicken, it constitutes 18 cm /g of body weight.
tubular air capillaries (pneumo-capillaries).
The diameter of the air capillaries, characteristic for Air sacs (sacci pneumatici, sacci aerophori)
each species, ranges from 3 to 10 μm. Due to the high The air sacs are thin-walled deformable cavities. They
surface tension within these small-calibre tubes, their are joined by connective tissue with adjacent organs or
diameter remains relatively constant. The air capillaries muscles but can also be partially covered with a tunica
are intimately intermeshed with a dense network of blood serosa. By penetrating the bones, the air sacs also serve to
capillaries, permitting gas exchange to take place. The pneumatise the skeleton. The walls of the air sacs con-
avian blood–air barrier is considerably thinner than that tain collagen and elastic fibres, as well as smooth muscle
of mammals and consists of three elements: cells.
Vet Histology.indb 257 16/07/2019 15:03