Page 319 - Veterinary Histology of Domestic Mammals and Birds, 5th Edition
P. 319
Female reproductive system 14
VetBooks.ir
(organa genitalia feminina)
The female reproductive organs of domestic mammals are tubae uterinae). This gives rise to the zygote from which
comprised of the: the embryo forms. The newly formed embryo passes
through the uterine tube into the uterus, where it becomes
· paired ovaries (ovaria), implanted in the mucosa (nidation, implantation) and
· paired uterine tubes (tubae uterinae), continues its embryonic and fetal development. During
· uterus and cervix pregnancy, the mucosa of the uterus undergoes species-
· vagina and vestibule (vestibulum vaginae) and dependent modifications and contributes to the formation
· vulva. of the placenta (refer to embryology texts).
The cervix, vagina, vestibule and vulva constitute the
The ovaries are the site of development and maturation birth canal. The vagina and labia of the vulva represent the
of female germ cells. In addition, the ovaries function external genitalia and copulatory organs.
as endocrine glands, synthesising several sex hormones In sexually mature animals, the organs of the female
including oestrogen, progesterone, testosterone and other reproductive tract undergo cyclic changes in structure.
androgens. At certain stages of the reproductive cycle, and These are most pronounced in the parenchyma of the
during pregnancy, a hormone-producing corpus luteum ovary and in the mucosa of individual organs.
(or several corpora lutea, in multi-ovulatory species) is
(are) formed in the ovary. Ovary (ovar, ovarium)
The uterine tubes transport germ cells, including In sexually mature domestic mammals, the ovaries have
the ova of the female and the spermatozoa of the male. two main functions: production of mature oocytes and
Union of the two haploid germ cells (fertilisation) occurs synthesis of reproductive hormones (Figure 14.1). Both
in the proximal segment of the uterine tubes (ampulla are subject to cyclic influences, mediated by feedback
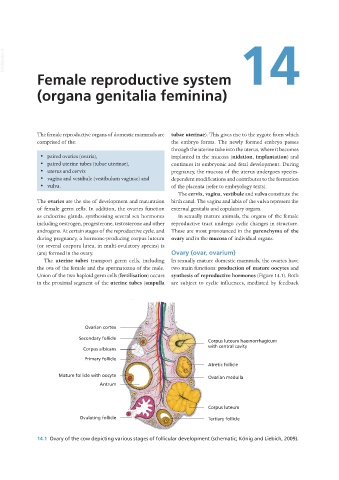
14.1 Ovary of the cow depicting various stages of follicular development (schematic; König and Liebich, 2009).
Vet Histology.indb 301 16/07/2019 15:05