Page 345 - Veterinary Histology of Domestic Mammals and Birds, 5th Edition
P. 345
Common integument (integumentum commune) 327
VetBooks.ir
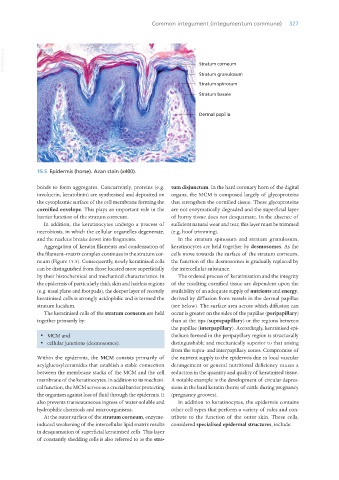
15.5 Epidermis (horse). Azan stain (x400).
bonds to form aggregates. Concurrently, proteins (e.g. tum disjunctum. In the hard coronary horn of the digital
involucrin, keratolinin) are synthesised and deposited on organs, the MCM is composed largely of glycoproteins
the cytoplasmic surface of the cell membrane forming the that strengthen the cornified tissue. These glycoproteins
cornified envelope. This plays an important role in the are not enzymatically degraded and the superficial layer
barrier function of the stratum corneum. of horny tissue does not desquamate. In the absence of
In addition, the keratinocytes undergo a process of sufficient natural wear and tear, this layer must be trimmed
necrobiosis, in which the cellular organelles degenerate, (e.g. hoof trimming).
and the nucleus breaks down into fragments. In the stratum spinosum and stratum granulosum,
Aggregation of keratin filaments and condensation of keratinocytes are held together by desmosomes. As the
the filament–matrix complex continues in the stratum cor- cells move towards the surface of the stratum corneum,
neum (Figure 15.5). Consequently, newly keratinised cells the function of the desmosomes is gradually replaced by
can be distinguished from those located more superficially the intercellular substance.
by their histochemical and mechanical characteristics. In The ordered process of keratinisation and the integrity
the epidermis of particularly thick skin and hairless regions of the resulting cornified tissue are dependent upon the
(e.g. nasal plane and foot pads), the deeper layer of recently availability of an adequate supply of nutrients and energy,
keratinised cells is strongly acidophilic and is termed the derived by diffusion from vessels in the dermal papillae
stratum lucidum. (see below). The surface area across which diffusion can
The keratinised cells of the stratum corneum are held occur is greater on the sides of the papillae (peripapillary)
together primarily by: than at the tips (suprapapillary) or the regions between
the papillae (interpapillary). Accordingly, keratinised epi-
· MCM and thelium formed in the peripapillary region is structurally
· cellular junctions (desmosomes). distinguishable and mechanically superior to that arising
from the supra- and interpapillary zones. Compromise of
Within the epidermis, the MCM consists primarily of the nutrient supply to the epidermis due to local vascular
acylglucosylceramides that establish a stable connection derangement or general nutritional deficiency causes a
between the membrane stacks of the MCM and the cell reduction in the quantity and quality of keratinised tissue.
membrane of the keratinocytes. In addition to its mechani- A notable example is the development of circular depres-
cal function, the MCM serves as a crucial barrier protecting sions in the hard keratin (horn) of cattle during pregnancy
the organism against loss of fluid through the epidermis. It (pregnancy grooves).
also prevents transcutaneous ingress of water-soluble and In addition to keratinocytes, the epidermis contains
hydrophilic chemicals and microorganisms. other cell types that perform a variety of roles and con-
At the outer surface of the stratum corneum, enzyme- tribute to the function of the outer skin. These cells,
induced weakening of the intercellular lipid matrix results considered specialised epidermal structures, include:
in desquamation of superficial keratinised cells. This layer
of constantly shedding cells is also referred to as the stra-
Vet Histology.indb 327 16/07/2019 15:06