Page 341 - Veterinary Histology of Domestic Mammals and Birds, 5th Edition
P. 341
Female reproductive system (organa genitalia feminina) 323
VetBooks.ir
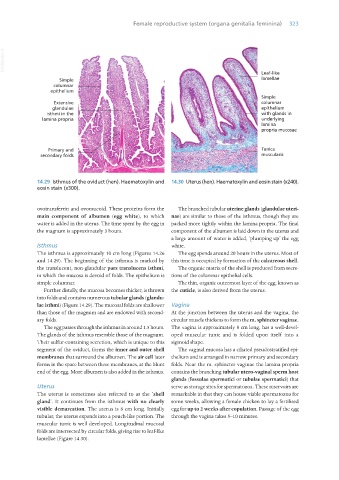
14.29 Isthmus of the oviduct (hen). Haematoxylin and 14.30 Uterus (hen). Haematoxylin and eosin stain (x240).
eosin stain (x300).
ovotransferrin and ovomucoid. These proteins form the The branched tubular uterine glands (glandulae uteri-
main component of albumen (egg white), to which nae) are similar to those of the isthmus, though they are
water is added in the uterus. The time spent by the egg in packed more tightly within the lamina propria. The final
the magnum is approximately 3 hours. component of the albumen is laid down in the uterus and
a large amount of water is added, ‘plumping up’ the egg
Isthmus white.
The isthmus is approximately 10 cm long (Figures 14.26 The egg spends around 20 hours in the uterus. Most of
and 14.29). The beginning of the isthmus is marked by this time is occupied by formation of the calcareous shell.
the translucent, non-glandular pars translucens isthmi, The organic matrix of the shell is produced from secre-
in which the mucosa is devoid of folds. The epithelium is tions of the columnar epithelial cells.
simple columnar. The thin, organic outermost layer of the egg, known as
Further distally, the mucosa becomes thicker, is thrown the cuticle, is also derived from the uterus.
into folds and contains numerous tubular glands (glandu-
lae isthmi) (Figure 14.29). The mucosal folds are shallower Vagina
than those of the magnum and are endowed with second- At the junction between the uterus and the vagina, the
ary folds. circular muscle thickens to form the m. sphincter vaginae.
The egg passes through the isthmus in around 1.5 hours. The vagina is approximately 8 cm long, has a well-devel-
The glands of the isthmus resemble those of the magnum. oped muscular tunic and is folded upon itself into a
Their sulfur-containing secretion, which is unique to this sigmoid shape.
segment of the oviduct, forms the inner and outer shell The vaginal mucosa has a ciliated pseudostratified epi-
membranes that surround the albumen. The air cell later thelium and is arranged in narrow primary and secondary
forms in the space between these membranes, at the blunt folds. Near the m. sphincter vaginae the lamina propria
end of the egg. More albumen is also added in the isthmus. contains the branching tubular utero-vaginal sperm host
glands (fossulae spermatici or tubulae spermatici) that
Uterus serve as storage sites for spermatozoa. These reservoirs are
The uterus is sometimes also referred to as the ‘shell remarkable in that they can house viable spermatozoa for
gland’. It continues from the isthmus with no clearly some weeks, allowing a female chicken to lay a fertilised
visible demarcation. The uterus is 8 cm long. Initially egg for up to 2 weeks after copulation. Passage of the egg
tubular, the uterus expands into a pouch-like portion. The through the vagina takes 5–10 minutes.
muscular tunic is well developed. Longitudinal mucosal
folds are intersected by circular folds, giving rise to leaf-like
lamellae (Figure 14.30).
Vet Histology.indb 323 16/07/2019 15:05