Page 337 - Veterinary Histology of Domestic Mammals and Birds, 5th Edition
P. 337
Female reproductive system (organa genitalia feminina) 319
VetBooks.ir
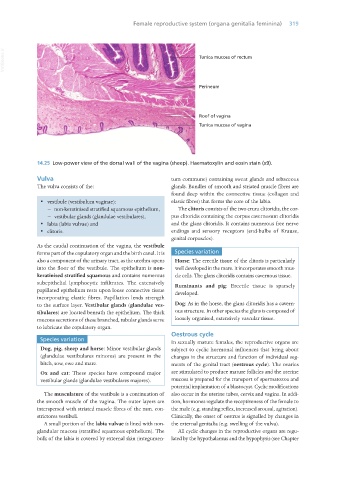
14.25 Low-power view of the dorsal wall of the vagina (sheep). Haematoxylin and eosin stain (x9).
Vulva tum commune) containing sweat glands and sebaceous
The vulva consists of the: glands. Bundles of smooth and striated muscle fibres are
found deep within the connective tissue (collagen and
· vestibule (vestibulum vaginae): elastic fibres) that forms the core of the labia.
− non-keratinised stratified squamous epithelium, The clitoris consists of the two crura clitoridis, the cor-
− vestibular glands (glandulae vestibulares), pus clitoridis containing the corpus cavernosum clitoridis
· labia (labia vulvae) and and the glans clitoridis. It contains numerous free nerve
· clitoris. endings and sensory receptors (end-bulbs of Krause,
genital corpuscles).
As the caudal continuation of the vagina, the vestibule
forms part of the copulatory organ and the birth canal. It is Species variation
also a component of the urinary tract, as the urethra opens Horse: The erectile tissue of the clitoris is particularly
into the floor of the vestibule. The epithelium is non- well developed in the mare. It incorporates smooth mus-
keratinised stratified squamous and contains numerous cle cells. The glans clitoridis contains cavernous tissue.
subepithelial lymphocytic infiltrates. The extensively Ruminants and pig: Erectile tissue is sparsely
papillated epithelium rests upon loose connective tissue developed.
incorporating elastic fibres. Papillation lends strength
to the surface layer. Vestibular glands (glandulae ves- Dog: As in the horse, the glans clitoridis has a cavern-
tibulares) are located beneath the epithelium. The thick ous structure. In other species the glans is composed of
mucous secretions of these branched, tubular glands serve loosely organised, extensively vascular tissue.
to lubricate the copulatory organ.
Oestrous cycle
Species variation
In sexually mature females, the reproductive organs are
Dog, pig, sheep and horse: Minor vestibular glands subject to cyclic hormonal influences that bring about
(glandulae vestibulares minores) are present in the changes in the structure and function of individual seg-
bitch, sow, ewe and mare. ments of the genital tract (oestrous cycle). The ovaries
Ox and cat: These species have compound major are stimulated to produce mature follicles and the uterine
vestibular glands (glandulae vestibulares majores). mucosa is prepared for the transport of spermatozoa and
potential implantation of a blastocyst. Cyclic modifications
The musculature of the vestibule is a continuation of also occur in the uterine tubes, cervix and vagina. In addi-
the smooth muscle of the vagina. The outer layers are tion, hormones regulate the receptiveness of the female to
interspersed with striated muscle fibres of the mm. con- the male (e.g. standing reflex, increased arousal, agitation).
strictores vestibuli. Clinically, the onset of oestrus is signalled by changes in
A small portion of the labia vulvae is lined with non- the external genitalia (e.g. swelling of the vulva).
glandular mucosa (stratified squamous epithelium). The All cyclic changes in the reproductive organs are regu-
bulk of the labia is covered by external skin (integumen- lated by the hypothalamus and the hypophysis (see Chapter
Vet Histology.indb 319 16/07/2019 15:05