Page 333 - Veterinary Histology of Domestic Mammals and Birds, 5th Edition
P. 333
Female reproductive system (organa genitalia feminina) 315
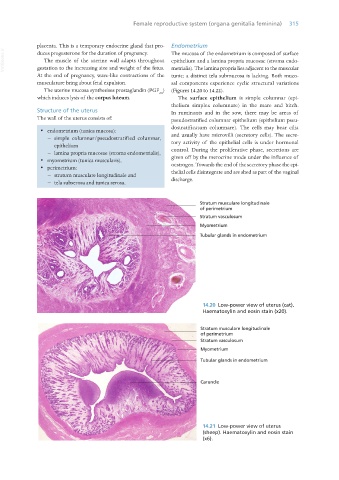
placenta. This is a temporary endocrine gland that pro- Endometrium
VetBooks.ir duces progesterone for the duration of pregnancy. The mucosa of the endometrium is composed of surface
The muscle of the uterine wall adapts throughout epithelium and a lamina propria mucosae (stroma endo-
gestation to the increasing size and weight of the fetus. metrialis). The lamina propria lies adjacent to the muscular
At the end of pregnancy, wave-like contractions of the tunic; a distinct tela submucosa is lacking. Both muco-
musculature bring about fetal expulsion. sal components experience cyclic structural variations
The uterine mucosa synthesises prostaglandin (PGF ) (Figures 14.20 to 14.22).
2α
which induces lysis of the corpus luteum. The surface epithelium is simple columnar (epi-
thelium simplex columnare) in the mare and bitch.
Structure of the uterus In ruminants and in the sow, there may be areas of
The wall of the uterus consists of: pseudostratified columnar epithelium (epithelium pseu-
dostratificatum columnare). The cells may bear cilia
· endometrium (tunica mucosa):
− simple columnar/pseudostratified columnar, and usually have microvilli (secretory cells). The secre-
epithelium tory activity of the epithelial cells is under hormonal
− lamina propria mucosae (stroma endometrialis), control. During the proliferative phase, secretions are
· myometrium (tunica muscularis), given off by the merocrine mode under the influence of
· perimetrium: oestrogen. Towards the end of the secretory phase the epi-
− stratum musculare longitudinale and thelial cells disintegrate and are shed as part of the vaginal
− tela subserosa and tunica serosa. discharge.
14.20 Low-power view of uterus (cat).
Haematoxylin and eosin stain (x20).
14.21 Low-power view of uterus
(sheep). Haematoxylin and eosin stain
(x6).
Vet Histology.indb 315 16/07/2019 15:05