Page 329 - Veterinary Histology of Domestic Mammals and Birds, 5th Edition
P. 329
Female reproductive system (organa genitalia feminina) 311
From early in its formation, the corpus luteum is per- Medulla (medulla ovarii, zona vasculosa)
VetBooks.ir vaded by a dense capillary network. The capillaries and In most species, the medulla is the inner portion of the
hairpin arteries contribute to lobulation of the corpus ovary enclosing blood vessels and nerves. Arteries enter
luteum. Connective tissue septa that subdivide the corpus at the hilus and are arranged in coils within the medulla.
luteum arise from the theca externa and, to a lesser degree, At the junction with the cortex, they form a plexus that
the theca interna. When the corpus luteum is actively supplies the cortical tissue. These capillary networks are
secreting hormones, the capillary loops are in close contact subject to cyclic structural changes regulated by specialised
with the luteal cells, facilitating the uptake of progesterone arteries (‘barrier arteries’) and arteriovenous anastomoses.
into the blood circulation. Medullary lymph vessels and veins leave the ovary at the
hilus. Predominantly autonomic nerve fibres innervate the
RegRession of the coRPus luteum follicles and smooth muscle cells of the blood vessel walls.
Regression of the corpus luteum is initiated by prostaglan-
din (PGF ) secreted by the uterine mucosa. Hypertrophy Species variation
2α
of blood vessel walls eventually results in blockage of the Ruminants: Rete ovarii originating from the mesoneph-
lumen and degeneration of the capillary network. This is ros are commonly present near the hilus. This is observed
accompanied by an increase in the amount of lipochrome less frequently in other species. The rete ovarii consists of
pigments in the luteal cells and merging and enlargement anastomosing cords and channels. These are composed of
of lipid vacuoles. The luteal cells undergo fatty degen- epithelium-like cells and are surrounded by a basal lamina.
eration, with associated karyolysis, and are broken down Horse: In the mare, the cortex lies internally, sur-
by macrophages. There is concurrent fibrosis (increase in rounded by the medulla. Cortical tissue is only present
collagen fibres). on the surface of the ovary at the ovulation fossa.
In the ox, regression begins from about 15 days after
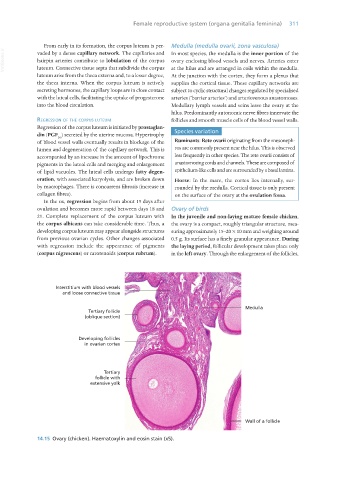
ovulation and becomes more rapid between days 18 and Ovary of birds
21. Complete replacement of the corpus luteum with In the juvenile and non-laying mature female chicken,
the corpus albicans can take considerable time. Thus, a the ovary is a compact, roughly triangular structure, mea-
developing corpus luteum may appear alongside structures suring approximately 15–20 × 10 mm and weighing around
from previous ovarian cycles. Other changes associated 0.5 g. Its surface has a finely granular appearance. During
with regression include the appearance of pigments the laying period, follicular development takes place only
(corpus nigrescens) or carotenoids (corpus rubrum). in the left ovary. Through the enlargement of the follicles,
14.15 Ovary (chicken). Haematoxylin and eosin stain (x5).
Vet Histology.indb 311 16/07/2019 15:05