Page 328 - Veterinary Histology of Domestic Mammals and Birds, 5th Edition
P. 328
310 Veterinary Histology of Domestic Mammals and Birds
VetBooks.ir
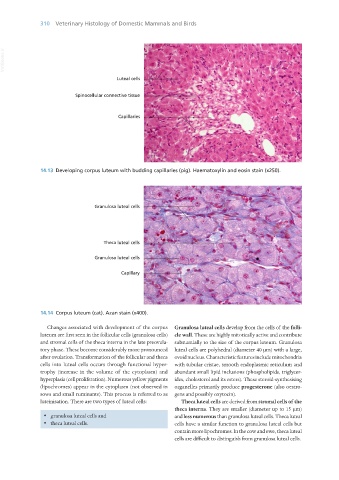
14.13 Developing corpus luteum with budding capillaries (pig). Haematoxylin and eosin stain (x250).
14.14 Corpus luteum (cat). Azan stain (x400).
Changes associated with development of the corpus Granulosa luteal cells develop from the cells of the folli-
luteum are first seen in the follicular cells (granulosa cells) cle wall. These are highly mitotically active and contribute
and stromal cells of the theca interna in the late preovula- substantially to the size of the corpus luteum. Granulosa
tory phase. These become considerably more pronounced luteal cells are polyhedral (diameter 40 μm) with a large,
after ovulation. Transformation of the follicular and theca ovoid nucleus. Characteristic features include mitochondria
cells into luteal cells occurs through functional hyper- with tubular cristae, smooth endoplasmic reticulum and
trophy (increase in the volume of the cytoplasm) and abundant small lipid inclusions (phospholipids, triglycer-
hyperplasia (cell proliferation). Numerous yellow pigments ides, cholesterol and its esters). These steroid-synthesising
(lipochromes) appear in the cytoplasm (not observed in organelles primarily produce progesterone (also oestro-
sows and small ruminants). This process is referred to as gens and possibly oxytocin).
luteinisation. There are two types of luteal cells: Theca luteal cells are derived from stromal cells of the
theca interna. They are smaller (diameter up to 15 μm)
· granulosa luteal cells and and less numerous than granulosa luteal cells. Theca luteal
· theca luteal cells. cells have a similar function to granulosa luteal cells but
contain more lipochromes. In the cow and ewe, theca luteal
cells are difficult to distinguish from granulosa luteal cells.
Vet Histology.indb 310 16/07/2019 15:05