Page 335 - Veterinary Histology of Domestic Mammals and Birds, 5th Edition
P. 335
Female reproductive system (organa genitalia feminina) 317
non-myelinated) extend from the stratum vasculosum into temporarily and close again. Dilation of the cervix dur-
VetBooks.ir the endometrium to supply the glands and the epithelium. ing oestrus facilitates the passage of spermatozoa to the
uterine tubes. Considerable amounts of mucus are pro-
Perimetrium
duced at this time. The cervix closes during dioestrus
The perimetrium surrounds the myometrium. It con- (corpus luteum cyclicum and corpus luteum gravidita-
sists of an outer tunica serosa, comprising a single layer tis) under the influence of progesterone. A mucous seal
of mesothelium, underlaid by a tela subserosa and a forms at its distal end, providing additional protection
well-developed layer of longitudinally oriented smooth against entry by spermatozoa and foreign agents (e.g. bac-
muscle fibres (stratum musculare longitudinale). The teria). During parturition, the cervix dilates markedly to
muscle radiates into the broad ligament of the uterus and is allow the passage of the fetus. The structure of the cervix
continuous with the muscle of the cervix. includes special features that accommodate these diverse
functions.
Cervix (cervix uteri) The cervix is composed of layers. These are thick in
The cervix is the distal continuation of the body of the ruminants (Figures 14.23 and 14.24), and relatively thin in
uterus. To perform its functions, the cervix must open the pig.
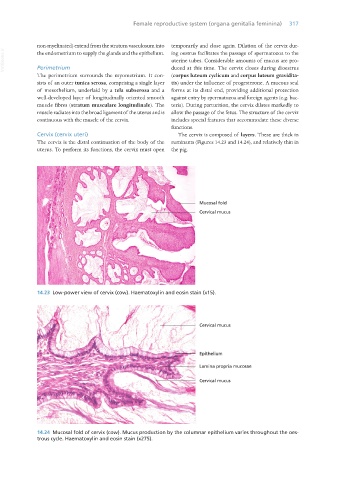
14.23 Low-power view of cervix (cow). Haematoxylin and eosin stain (x15).
14.24 Mucosal fold of cervix (cow). Mucus production by the columnar epithelium varies throughout the oes-
trous cycle. Haematoxylin and eosin stain (x275).
Vet Histology.indb 317 16/07/2019 15:05