Page 162 - Feline diagnostic imaging
P. 162
10.3 iggt arasternal Sgort AAis Viees 163
(b)
(a)
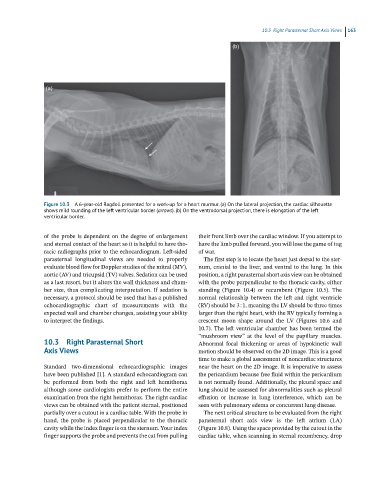
Figure 10.3 A 6-year-old Ragdoll presented for a work-up for a heart murmur. (a) On the lateral projection, the cardiac silhouette
shows mild rounding of the left ventricular border (arroes). (b) On the ventrodorsal projection, there is elongation of the left
ventricular border.
of the probe is dependent on the degree of enlargement their front limb over the cardiac window. If you attempt to
and sternal contact of the heart so it is helpful to have tho- have the limb pulled forward, you will lose the game of tug
racic radiographs prior to the echocardiogram. Left‐sided of war.
parasternal longitudinal views are needed to properly The first step is to locate the heart just dorsal to the ster-
evaluate blood flow for Doppler studies of the mitral (MV), num, cranial to the liver, and ventral to the lung. In this
aortic (AV) and tricupsid (TV) valves. Sedation can be used position, a right parasternal short axis view can be obtained
as a last resort, but it alters the wall thickness and cham- with the probe perpendicular to the thoracic cavity, either
ber size, thus complicating interpretation. If sedation is standing (Figure 10.4) or recumbent (Figure 10.5). The
necessary, a protocol should be used that has a published normal relationship between the left and right ventricle
echocardiographic chart of measurements with the (RV) should be 3 : 1, meaning the LV should be three times
expected wall and chamber changes, assisting your ability larger than the right heart, with the RV typically forming a
to interpret the findings. crescent moon shape around the LV (Figures 10.6 and
10.7). The left ventricular chamber has been termed the
“mushroom view” at the level of the papillary muscles.
10.3 Right Parasternal Short Abnormal focal thickening or areas of hypokinetic wall
Axis Views motion should be observed on the 2D image. This is a good
time to make a global assessment of noncardiac structures
Standard two‐dimensional echocardiographic images near the heart on the 2D image. It is imperative to assess
have been published [1]. A standard echocardiogram can the pericardium because free fluid within the pericardium
be performed from both the right and left hemithorax is not normally found. Additionally, the pleural space and
although some cardiologists prefer to perform the entire lung should be assessed for abnormalities such as pleural
examination from the right hemithorax. The right cardiac effusion or increase in lung interference, which can be
views can be obtained with the patient sternal, positioned seen with pulmonary edema or concurrent lung disease.
partially over a cutout in a cardiac table. With the probe in The next critical structure to be evaluated from the right
hand, the probe is placed perpendicular to the thoracic parasternal short axis view is the left atrium (LA)
cavity while the index finger is on the sternum. Your index (Figure 10.8). Using the space provided by the cutout in the
finger supports the probe and prevents the cat from pulling cardiac table, when scanning in sternal recumbency, drop