Page 164 - Feline diagnostic imaging
P. 164
10.4 iggt arasternal Long AAis Viees 165
Figure 10.9 Image showing hand position while a cat is
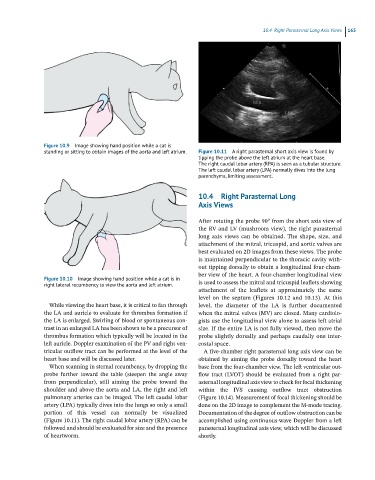
standing or sitting to obtain images of the aorta and left atrium. Figure 10.11 A right parasternal short axis view is found by
tipping the probe above the left atrium at the heart base.
The right caudal lobar artery (RPA) is seen as a tubular structure.
The left caudal lobar artery (LPA) normally dives into the lung
parenchyma, limiting assessment.
10.4 Right Parasternal Long
Axis Views
After rotating the probe 90° from the short axis view of
the RV and LV (mushroom view), the right parasternal
long axis views can be obtained. The shape, size, and
attachment of the mitral, tricuspid, and aortic valves are
best evaluated on 2D images from these views. The probe
is maintained perpendicular to the thoracic cavity with-
out tipping dorsally to obtain a longitudinal four‐cham-
ber view of the heart. A four‐chamber longitudinal view
Figure 10.10 Image showing hand position while a cat is in
right lateral recumbency to view the aorta and left atrium. is used to assess the mitral and tricuspid leaflets showing
attachment of the leaflets at approximately the same
level on the septum (Figures 10.12 and 10.13). At this
While viewing the heart base, it is critical to fan through level, the diameter of the LA is further documented
the LA and auricle to evaluate for thrombus formation if when the mitral valves (MV) are closed. Many cardiolo-
the LA is enlarged. Swirling of blood or spontaneous con- gists use the longitudinal view alone to assess left atrial
trast in an enlarged LA has been shown to be a precursor of size. If the entire LA is not fully viewed, then move the
thrombus formation which typically will be located in the probe slightly dorsally and perhaps caudally one inter-
left auricle. Doppler examination of the PV and right ven- costal space.
tricular outflow tract can be performed at the level of the A five‐chamber right parasternal long axis view can be
heart base and will be discussed later. obtained by aiming the probe dorsally toward the heart
When scanning in sternal recumbency, by dropping the base from the four‐chamber view. The left ventricular out-
probe further toward the table (steepen the angle away flow tract (LVOT) should be evaluated from a right par-
from perpendicular), still aiming the probe toward the asternal longitudinal axis view to check for focal thickening
shoulder and above the aorta and LA, the right and left within the IVS causing outflow tract obstruction
pulmonary arteries can be imaged. The left caudal lobar (Figure 10.14). Measurement of focal thickening should be
artery (LPA) typically dives into the lungs so only a small done on the 2D image to complement the M‐mode tracing.
portion of this vessel can normally be visualized Documentation of the degree of outflow obstruction can be
(Figure 10.11). The right caudal lobar artery (RPA) can be accomplished using continuous‐wave Doppler from a left
followed and should be evaluated for size and the presence parasternal longitudinal axis view, which will be discussed
of heartworm. shortly.