Page 168 - Feline diagnostic imaging
P. 168
10.5 MMMode 169
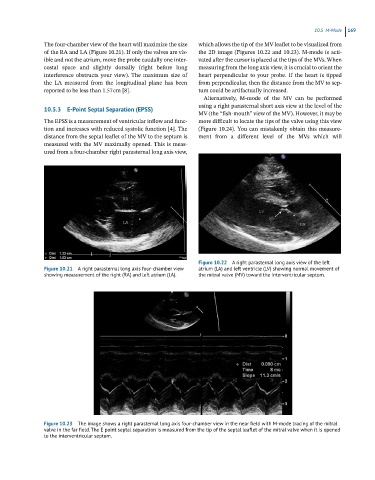
The four‐chamber view of the heart will maximize the size which allows the tip of the MV leaflet to be visualized from
of the RA and LA (Figure 10.21). If only the valves are vis- the 2D image (Figures 10.22 and 10.23). M‐mode is acti-
ible and not the atrium, move the probe caudally one inter- vated after the cursor is placed at the tips of the MVs. When
costal space and slightly dorsally (right before lung measuring from the long axis view, it is crucial to orient the
interference obstructs your view). The maximum size of heart perpendicular to your probe. If the heart is tipped
the LA measured from the longitudinal plane has been from perpendicular, then the distance from the MV to sep-
reported to be less than 1.57 cm [8]. tum could be artifactually increased.
Alternatively, M‐mode of the MV can be performed
using a right parasternal short axis view at the level of the
10.5.3 E-Point Septal Separation (EPSS)
MV (the “fish‐mouth” view of the MV). However, it may be
The EPSS is a measurement of ventricular inflow and func- more difficult to locate the tips of the valve using this view
tion and increases with reduced systolic function [4]. The (Figure 10.24). You can mistakenly obtain this measure-
distance from the septal leaflet of the MV to the septum is ment from a different level of the MVs which will
measured with the MV maximally opened. This is meas-
ured from a four‐chamber right parasternal long axis view,
Figure 10.22 A right parasternal long axis view of the left
Figure 10.21 A right parasternal long axis four-chamber view atrium (LA) and left ventricle (LV) showing normal movement of
showing measurement of the right (RA) and left atrium (LA). the mitral valve (MV) toward the interventricular septum.
Figure 10.23 The image shows a right parasternal long axis four-chamber view in the near field with M-mode tracing of the mitral
valve in the far field. The E point septal separation is measured from the tip of the septal leaflet of the mitral valve when it is opened
to the interventricular septum.