Page 166 - Feline diagnostic imaging
P. 166
10.5 MMMode 167
RVFW, right ventricular chamber, and IVS as separate
structures (Figure 10.16). Errors in measurement of the RV
and LV can occur if the imaging plane is not properly
located at the level of the papillary muscles. If the imaging
plane is slightly above the papillary muscles and the tips of
the MVs are in the 2D image (Figure 10.17), a decrease in
the fractional shortening (FS) on the M‐mode tracing may
be artifactually present because at this level the septal
motion is normally decreased. If the imaging plane is
below this region, the walls will appear thickened with a
significant decrease in left ventricular chamber size
(Figure 10.18).
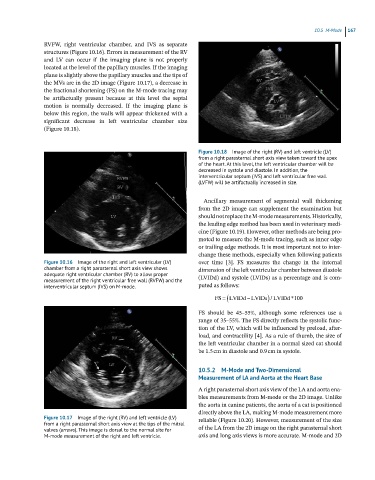
Figure 10.18 Image of the right (RV) and left ventricle (LV)
from a right parasternal short axis view taken toward the apex
of the heart. At this level, the left ventricular chamber will be
decreased in systole and diastole. In addition, the
interventricular septum (IVS) and left ventricular free wall
(LVFW) will be artifactually increased in size.
Ancillary measurement of segmental wall thickening
from the 2D image can supplement the examination but
should not replace the M‐mode measurements. Historically,
the leading edge method has been used in veterinary medi-
cine (Figure 10.19). However, other methods are being pro-
moted to measure the M‐mode tracing, such as inner edge
or trailing edge methods. It is most important not to inter-
change these methods, especially when following patients
Figure 10.16 Image of the right and left ventricular (LV) over time [3]. FS measures the change in the internal
chamber from a right parasternal short axis view shows dimension of the left ventricular chamber between diastole
adequate right ventricular chamber (RV) to allow proper (LVIDd) and systole (LVIDs) as a percentage and is com-
measurement of the right ventricular free wall (RVFW) and the
interventricular septum (IVS) on M-mode. puted as follows:
FS LVIDd LVIDs / LVIDd*100
FS should be 45–55%, although some references use a
range of 35–55%. The FS directly reflects the systolic func-
tion of the LV, which will be influenced by preload, after-
load, and contractility [4]. As a rule of thumb, the size of
the left ventricular chamber in a normal sized cat should
be 1.5 cm in diastole and 0.9 cm in systole.
10.5.2 M-Mode and Two-Dimensional
Measurement of LA and Aorta at the Heart Base
A right parasternal short axis view of the LA and aorta ena-
bles measurements from M‐mode or the 2D image. Unlike
the aorta in canine patients, the aorta of a cat is positioned
directly above the LA, making M‐mode measurement more
Figure 10.17 Image of the right (RV) and left ventricle (LV) reliable (Figure 10.20). However, measurement of the size
from a right parasternal short axis view at the tips of the mitral
valves (arroes). This image is dorsal to the normal site for of the LA from the 2D image on the right parasternal short
M-mode measurement of the right and left ventricle. axis and long axis views is more accurate. M‐mode and 2D