Page 54 - Feline diagnostic imaging
P. 54
50 5 Diagnostic Imaging of Diseases of the Skull
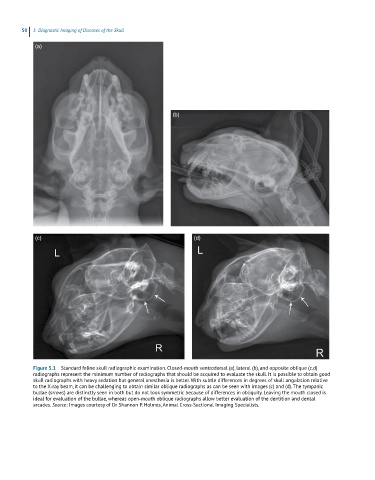
(a)
(b)
(c) (d)
Figure 5.1 Standard feline skull radiographic examination. Closed‐mouth ventrodorsal (a), lateral (b), and opposite oblique (c,d)
radiographs represent the minimum number of radiographs that should be acquired to evaluate the skull. It is possible to obtain good
skull radiographs with heavy sedation but general anesthesia is better. With subtle differences in degrees of skull angulation relative
to the X‐ray beam, it can be challenging to obtain similar oblique radiographs as can be seen with images (c) and (d). The tympanic
bullae (arrows) are distinctly seen in both but do not look symmetric because of differences in obliquity. Leaving the mouth closed is
ideal for evaluation of the bullae, whereas open‐mouth oblique radiographs allow better evaluation of the dentition and dental
arcades. Source: Images courtesy of Dr Shannon P. Holmes, Animal Cross‐Sectional Imaging Specialists.