Page 59 - Feline diagnostic imaging
P. 59
5.1 Diseases of the eline Skull 55
(a) (b)
(d)
(c)
(e)
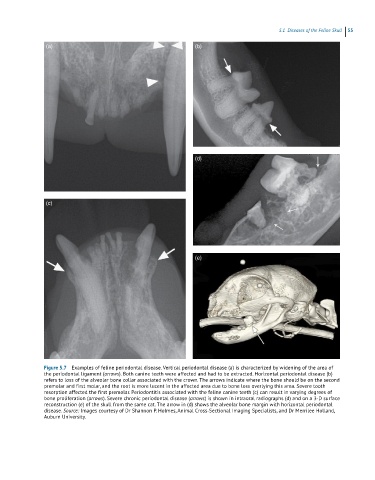
Figure 5.7 Examples of feline periodontal disease. Vertical periodontal disease (a) is characterized by widening of the area of
the periodontal ligament (arrows). Both canine teeth were affected and had to be extracted. Horizontal periodontal disease (b)
refers to loss of the alveolar bone collar associated with the crown. The arrows indicate where the bone should be on the second
premolar and first molar, and the root is more lucent in the affected area due to bone loss overlying this area. Severe tooth
resorption affected the first premolar. Periodontitis associated with the feline canine teeth (c) can result in varying degrees of
bone proliferation (arrows). Severe chronic periodontal disease (arrows) is shown in intraoral radiographs (d) and on a 3‐D surface
reconstruction (e) of the skull from the same cat. The arrow in (d) shows the alveolar bone margin with horizontal periodontal
disease. Source: Images courtesy of Dr Shannon P. Holmes, Animal Cross‐Sectional Imaging Specialists, and Dr Merrilee Holland,
Auburn University.