Page 100 - Veterinary Histology of Domestic Mammals and Birds, 5th Edition
P. 100
82 Veterinary Histology of Domestic Mammals and Birds
VetBooks.ir
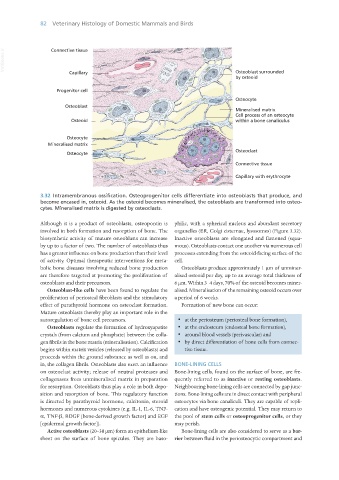
3.32 Intramembranous ossification. Osteoprogenitor cells differentiate into osteoblasts that produce, and
become encased in, osteoid. As the osteoid becomes mineralised, the osteoblasts are transformed into osteo-
cytes. Mineralised matrix is digested by osteoclasts.
Although it is a product of osteoblasts, osteopontin is philic, with a spherical nucleus and abundant secretory
involved in both formation and resorption of bone. The organelles (ER, Golgi cisternae, lysosomes) (Figure 3.32).
biosynthetic activity of mature osteoblasts can increase Inactive osteoblasts are elongated and flattened (squa-
by up to a factor of two. The number of osteoblasts thus mous). Osteoblasts contact one another via numerous cell
has a greater influence on bone production than their level processes extending from the osteoid-facing surface of the
of activity. Optimal therapeutic interventions for meta- cell.
bolic bone diseases involving reduced bone production Osteoblasts produce approximately 1 μm of unminer-
are therefore targeted at promoting the proliferation of alised osteoid per day, up to an average total thickness of
osteoblasts and their precursors. 6 μm. Within 3–4 days, 70% of the osteoid becomes miner-
Osteoblast-like cells have been found to regulate the alised. Mineralisation of the remaining osteoid occurs over
proliferation of periosteal fibroblasts and the stimulatory a period of 6 weeks.
effect of parathyroid hormone on osteoclast formation. Formation of new bone can occur:
Mature osteoblasts thereby play an important role in the
autoregulation of bone cell precursors. · at the periosteum (periosteal bone formation),
Osteoblasts regulate the formation of hydroxyapatite · at the endosteum (endosteal bone formation),
crystals (from calcium and phosphate) between the colla- · around blood vessels (perivascular) and
gen fibrils in the bone matrix (mineralisation). Calcification · by direct differentiation of bone cells from connec-
begins within matrix vesicles (released by osteoblasts) and tive tissue.
proceeds within the ground substance as well as on, and
in, the collagen fibrils. Osteoblasts also exert an influence BONE-LINING CELLS
on osteoclast activity; release of neutral proteases and Bone-lining cells, found on the surface of bone, are fre-
collagenases frees unmineralised matrix in preparation quently referred to as inactive or resting osteoblasts.
for resorption. Osteoblasts thus play a role in both depo- Neighbouring bone-lining cells are connected by gap junc-
sition and resorption of bone. This regulatory function tions. Bone-lining cells are in direct contact with peripheral
is directed by parathyroid hormone, calcitonin, steroid osteocytes via bone canaliculi. They are capable of repli-
hormones and numerous cytokines (e.g. IL-1, IL-6, TNF- cation and have osteogenic potential. They may return to
α, TNF-β, BDGF [bone-derived growth factor] and EGF the pool of stem cells or osteoprogenitor cells, or they
[epidermal growth factor]). may perish.
Active osteoblasts (20–30 μm) form an epithelium-like Bone-lining cells are also considered to serve as a bar-
sheet on the surface of bone spicules. They are baso- rier between fluid in the periosteocytic compartment and
Vet Histology.indb 82 16/07/2019 14:56