Page 193 - Veterinary Histology of Domestic Mammals and Birds, 5th Edition
P. 193
Endocrine system (systema endocrinum) 175
VetBooks.ir
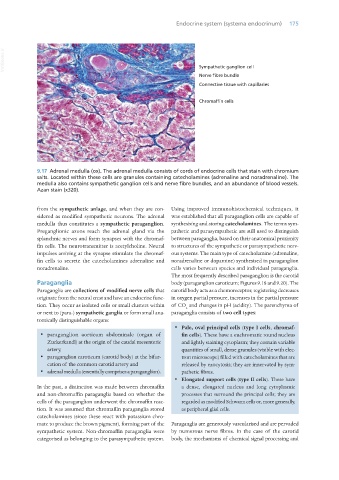
9.17 Adrenal medulla (ox). The adrenal medulla consists of cords of endocrine cells that stain with chromium
salts. Located within these cells are granules containing catecholamines (adrenaline and noradrenaline). The
medulla also contains sympathetic ganglion cells and nerve fibre bundles, and an abundance of blood vessels.
Azan stain (x320).
from the sympathetic anlage, and when they are con- Using improved immunohistochemical techniques, it
sidered as modified sympathetic neurons. The adrenal was established that all paraganglion cells are capable of
medulla thus constitutes a sympathetic paraganglion. synthesising and storing catecholamines. The terms sym-
Preganglionic axons reach the adrenal gland via the pathetic and parasympathetic are still used to distinguish
splanchnic nerves and form synapses with the chromaf- between paraganglia, based on their anatomical proximity
fin cells. The neurotransmitter is acetylcholine. Neural to structures of the sympathetic or parasympathetic nerv-
impulses arriving at the synapse stimulate the chromaf- ous systems. The main type of catecholamine (adrenaline,
fin cells to secrete the catecholamines adrenaline and noradrenaline or dopamine) synthesised in paraganglion
noradrenaline. cells varies between species and individual paraganglia.
The most frequently described paraganglion is the carotid
Paraganglia body (paraganglion caroticum; Figures 9.18 and 9.20). The
Paraganglia are collections of modified nerve cells that carotid body acts as a chemoreceptor, registering decreases
originate from the neural crest and have an endocrine func- in oxygen partial pressure, increases in the partial pressure
tion. They occur as isolated cells or small clusters within of CO and changes in pH (acidity). The parenchyma of
2
or next to (para-) sympathetic ganglia or form small ana- paraganglia consists of two cell types:
tomically distinguishable organs:
· Pale, oval principal cells (type I cells, chromaf-
· paraganglion aorticum abdominale (organ of fin cells). These have a euchromatic round nucleus
Zuckerkandl) at the origin of the caudal mesenteric and lightly staining cytoplasm; they contain variable
artery, quantities of small, dense granules (visible with elec-
· paraganglion caroticum (carotid body) at the bifur- tron microscope) filled with catecholamines that are
cation of the common carotid artery and released by exocytosis; they are innervated by sym-
· adrenal medulla (essentially comprises a paraganglion). pathetic fibres.
· Elongated support cells (type II cells). These have
In the past, a distinction was made between chromaffin a dense, elongated nucleus and long cytoplasmic
and non-chromaffin paraganglia based on whether the processes that surround the principal cells; they are
cells of the paraganglion underwent the chromaffin reac- regarded as modified Schwann cells or, more generally,
tion. It was assumed that chromaffin paraganglia stored as peripheral glial cells.
catecholamines (since these react with potassium chro-
mate to produce the brown pigment), forming part of the Paraganglia are generously vascularised and are pervaded
sympathetic system. Non-chromaffin paraganglia were by numerous nerve fibres. In the case of the carotid
categorised as belonging to the parasympathetic system. body, the mechanisms of chemical signal processing and
Vet Histology.indb 175 16/07/2019 15:00