Page 88 - Veterinary Histology of Domestic Mammals and Birds, 5th Edition
P. 88
70 Veterinary Histology of Domestic Mammals and Birds
VetBooks.ir
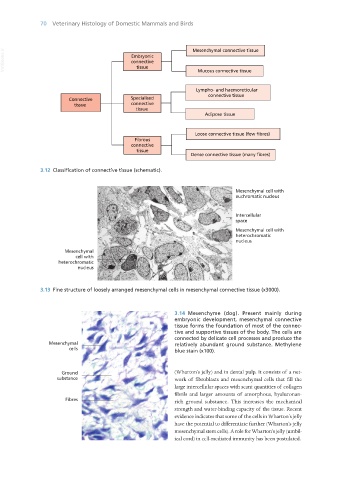
3.12 Classification of connective tissue (schematic).
3.13 Fine structure of loosely arranged mesenchymal cells in mesenchymal connective tissue (x3000).
3.14 Mesenchyme (dog). Present mainly during
embryonic development, mesenchymal connective
tissue forms the foundation of most of the connec-
tive and supportive tissues of the body. The cells are
connected by delicate cell processes and produce the
relatively abundant ground substance. Methylene
blue stain (x100).
(Wharton’s jelly) and in dental pulp. It consists of a net-
work of fibroblasts and mesenchymal cells that fill the
large intercellular spaces with scant quantities of collagen
fibrils and larger amounts of amorphous, hyaluronan-
rich ground substance. This increases the mechanical
strength and water-binding capacity of the tissue. Recent
evidence indicates that some of the cells in Wharton’s jelly
have the potential to differentiate further (Wharton’s jelly
mesenchymal stem cells). A role for Wharton’s jelly (umbil-
ical cord) in cell-mediated immunity has been postulated.
Vet Histology.indb 70 16/07/2019 14:55