Page 86 - Veterinary Histology of Domestic Mammals and Birds, 5th Edition
P. 86
68 Veterinary Histology of Domestic Mammals and Birds
space (Figure 3.6). In lymphoreticular tissues, reticular
VetBooks.ir fibres are produced by specialised reticular cells with which
they are in close contact.
Reticular fibrils (diameter 20–40 nm) exhibit cross-stri-
ations with a periodicity of 64–68 nm (as do collagen type
I fibrils). Reticular fibres are delicate, measuring just 0.2–1
μm in diameter. Their surface is coated with proteoglycans
and glycoprotein-rich substances (Table 3.1).
Under light microscopy, reticular fibres can be identified
using the PAS reaction, or by superficial impregnation with
silver salts (argyrophilic staining).
ELASTIC FIBRES (FIBRA ELASTICA)
Elastic fibres are primarily distinguished from collagen
fibres by their pronounced elasticity (can be stretched to
150% of their original length) and their marked refrac-
tivity (Figure 3.9). Elastic fibres exhibit branching and
combine to form irregularly expanded networks or
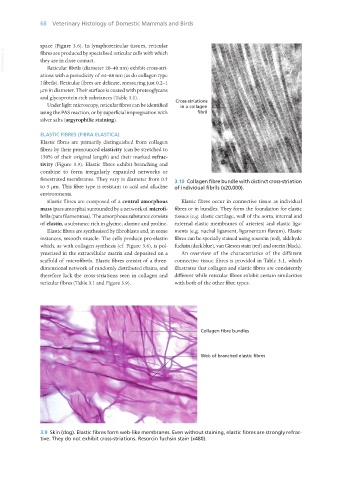
fenestrated membranes. They vary in diameter from 0.5 3.10 Collagen fibre bundle with distinct cross-striation
to 5 μm. This fibre type is resistant to acid and alkaline of individual fibrils (x20,000).
environments.
Elastic fibres are composed of a central amorphous Elastic fibres occur in connective tissue as individual
mass (pars amorpha) surrounded by a network of microfi- fibres or in bundles. They form the foundation for elastic
brils (pars filamentosa). The amorphous substance consists tissues (e.g. elastic cartilage, wall of the aorta, internal and
of elastin, a substance rich in glycine, alanine and proline. external elastic membranes of arteries) and elastic liga-
Elastic fibres are synthesised by fibroblasts and, in some ments (e.g. nuchal ligament, ligamentum flavum). Elastic
instances, smooth muscle. The cells produce pro-elastin fibres can be specially stained using resorcin (red), aldehyde
which, as with collagen synthesis (cf. Figure 3.6), is pol- fuchsin (dark blue), van Gieson stain (red) and orcein (black).
ymerised in the extracellular matrix and deposited on a An overview of the characteristics of the different
scaffold of microfibrils. Elastic fibres consist of a three- connective tissue fibres is provided in Table 3.1, which
dimensional network of randomly distributed chains, and illustrates that collagen and elastic fibres are consistently
therefore lack the cross-striations seen in collagen and different while reticular fibres exhibit certain similarities
reticular fibres (Table 3.1 and Figure 3.9). with both of the other fibre types.
3.9 Skin (dog). Elastic fibres form web-like membranes. Even without staining, elastic fibres are strongly refrac-
tive. They do not exhibit cross-striations. Resorcin fuchsin stain (x480).
Vet Histology.indb 68 16/07/2019 14:55