Page 101 - MHF-FeedingMinds-final.indd
P. 101
92
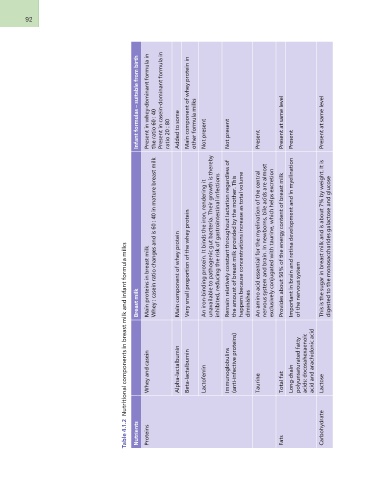
Table 4.1.2 Nutritional components in breast milk and infant formula milks
Nutrients Breast milk Infant formulas – suitable from birth
Proteins Whey and casein Main proteins in breast milk Present in whey-dominant formula in
Whey : casein ratio changes and is 60 : 40 in mature breast milk the ratio 60 : 40
Fats Alpha-lactalbumin Present in casein-dominant formula in
Carbohydrate Beta-lactalbumin Main component of whey protein ratio 20 : 80
Very small proportion of the whey protein Added to some
Lactoferrin Main component of whey protein in
An iron-binding protein. It binds the iron, rendering it other formula milks
Immunoglobulins unavailable to pathogenic gut bacteria. Their growth is thereby Not present
(anti-infective proteins) inhibited, reducing the risk of gastrointestinal infections
Remain relatively constant throughout lactation regardless of Not present
Taurine the amount of breast milk provided by the mother. This
happens because concentrations increase as total volume Present
Total fat diminishes
Long-chain An amino acid essential for the myelination of the central Present at same level
polyunsaturated fatty nervous system and brain. In newborns, bile acids are almost Present
acids: docosahexaenoic exclusively conjugated with taurine, which helps excretion
acid and arachidonic acid Provides about 50% of the energy content of breast milk
Lactose Important in brain and retina development and in myelination
of the nervous system
This is the sugar in breast milk and is about 7% by weight. It is Present at same level
digested to the monosaccharides galactose and glucose