Page 102 - MHF-FeedingMinds-final.indd
P. 102
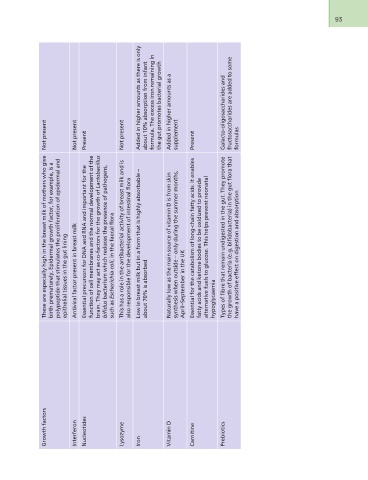
Growth factors These are especially high in the breast milk of mothers who give Not present
birth prematurely. Epidermal growth factor, for example, is a
Interferon polypeptide that stimulates the proliferation of epidermal and
Nucleotides epithelial tissues in the gut lining
Lysozyme Antiviral factor present in breast milk Not present
Iron
Essential precursors for DNA and RNA and important for the Present
Vitamin D function of cell membranes and the normal development of the
Carnitine brain. They may act as co-factors for the growth of Lactobacillus
bifidus bacterium which reduces the presence of pathogens,
Prebiotics such as Escherichia coli, in the faecal flora
This has a role in the antibacterial activity of breast milk and is Not present
also responsible for the development of intestinal flora
Low in breast milk but in a form that is highly absorbable – Added in higher amounts as there is only
about 70% is absorbed about 10% absorption from infant
formula. The excess iron remaining in
the gut promotes bacterial growth
Naturally low as the main source of vitamin D is from skin Added in higher amounts as a
synthesis when outside – only during the summer months, supplement
April–September in the UK
Essential for the catabolism of long-chain fatty acids. It enables Present
fatty acids and ketone bodies to be oxidized to provide
alternative fuels to glucose. This helps prevent neonatal
hypoglycaemia
Types of fibre that remain undigested in the gut. They promote Galacto-oligosaccharides and
the growth of bacteria (e.g. bifidobacteria) in the gut flora that fructosaccharides are added to some
have a positive effect on digestion and absorption formulas
93