Page 240 - MHF-FeedingMinds-final.indd
P. 240
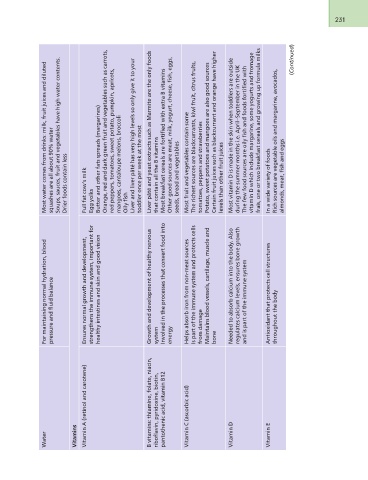
Water For maintaining normal hydration, blood Most water comes from drinks: milk, fruit juices and diluted
Vitamins pressure and fluid balance squashes are all about 90% water
Vitamin A (retinol and carotene) Soups, sauces, fruit and vegetables have high water contents.
Drier foods contain less
B vitamins: thiamine, folate, niacin,
riboflavin, pyridoxine, biotin, Ensures normal growth and development, Full fat cow’s milk
pantothenic acid, vitamin B12 strengthens the immune system, important for Egg yolks
Vitamin C (ascorbic acid) healthy intestines and skin and good vision Butter and other fats spreads (margarines)
Orange, red and dark green fruit and vegetables such as carrots,
Vitamin D Growth and development of healthy nervous red peppers, tomatoes, sweet potato, pumpkin, apricots,
system mangoes, cantaloupe melons, broccoli
Vitamin E Involved in the processes that convert food into Oily fish
energy Liver and liver pâté has very high levels so only give it to your
toddler once per week at the most
Helps absorb iron from non-meat sources
Is part of the immune system and protects cells Liver pâté and yeast extracts such as Marmite are the only foods
from damage that contain all the B vitamins
Maintains blood vessels, cartilage, muscle and Most breakfast cereals are fortified with extra B vitamins
bone Other good sources are meat, milk, yogurt, cheese, fish, eggs,
seeds, bread and vegetables
Needed to absorb calcium into the body. Also
regulates calcium levels, ensures bone growth Most fruit and vegetables contain some
and is part of the immune system The richest sources are blackcurrants, kiwi fruit, citrus fruits,
tomatoes, peppers and strawberries
Antioxidant that protects cell structures Potato, sweet potatoes and mangoes are also good sources
throughout the body Certain fruit juices such as blackcurrant and orange have higher
levels than other fruit juices
Most vitamin D is made in the skin when toddlers are outside
during the summer months i.e. April–September in the UK
The few food sources are oily fish and foods fortified with
vitamin D which include margarine, some yogurts and fromage
frais, one or two breakfast cereals and growing up formula milks
In a wide variety of foods
Rich sources are vegetable oils and margarine, avocados,
almonds, meat, fish and eggs
(Continued)
231