Page 239 - MHF-FeedingMinds-final.indd
P. 239
230
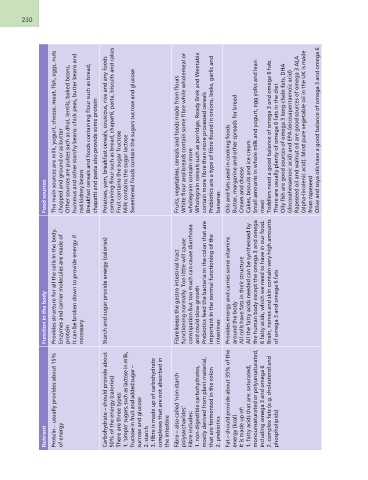
Nutrient Function in the body Food sources
Provides structure for all the cells in the body.
Protein – usually provides about 15% Enzymes and carrier molecules are made of The main sources are milk, yogurt, cheese, meat, fish, eggs, nuts
of energy protein chopped and ground or as butter
It can be broken down to provide energy if Other sources are pulses such as dhal, lentils, baked beans,
Carbohydrate – should provide about necessary hummus and other starchy beans: chick peas, butter beans and
50% of the energy (calories) red kidney beans
There are three types: Starch and sugar provide energy (calories) Breakfast cereals and foods containing flour such as bread,
1. ‘simple’ sugars, such as lactose in milk, chapatti and pasta also provide some protein
fructose in fruit and added sugar – Fibre keeps the gastro intestinal tract
sucrose and glucose functioning normally. Too little will cause Potatoes, yam, breakfast cereals, couscous, rice and any foods
2. starch constipation but too much can cause diarrhoea containing flour such as bread, chapatti, pasta, biscuits and cakes
3. fibre is made up of carbohydrate and could slow growth Fruit contains the sugar fructose
complexes that are not absorbed in Prebiotics feed the bacteria in the colon that are Milk contains the sugar lactose
the intestine important in the normal functioning of the Sweetened foods contain the sugars sucrose and glucose
intestines
Fibre – also called ‘non-starch Provides energy and carries some vitamins Fruits, vegetables, cereals and foods made from flours
polysaccharides’ around the body White flour and breads contain some fibre while wholemeal or
Fibre includes: All cells have fats in their structure wholegrain contain more
1. non-digestible carbohydrates, All the fatty acids needed can be synthesised by Wholegrain cereals such as porridge, Ready Brek and Weetabix
mostly derived from plant material, the human body except the omega 3 and omega contain more fibre than more processed cereals
that are fermented in the colon 6 fatty acids, which we need to have in our food. Prebiotics are a type of fibre found in onions, leeks, garlic and
2. prebiotics Brain, nerves and skin contain very high amounts bananas
of omega 3 and omega 6 fats
Fat – should provide about 35% of the Oils and fats used in cooking foods
energy (kcal) Butter, margarine and other spreads for bread
It is made up of: Cream and cheese
1. fatty acids that are: saturated, Cakes, biscuits and ice cream
monounsaturated or polyunsaturated, Small amounts in whole milk and yogurt, egg yolks and lean
including omega 3 and omega 6 meat
2. complex fats (e.g. cholesterol and Toddlers need a good balance of omega 3 and omega 6 fats.
phospholipids) There are usually plenty of omega 6 fats in the diet
Oily fish are good sources of omega 3 long-chain fats, DHA
(docosahexaenoic acid) and EPA (eicosapentaenoic acid)
Rapeseed oil and walnut oil are good sources of omega 3 ALA
(alpha-linolenic acid). Most pure vegetable oil in the UK is made
from rapeseed
Olive and soya oils have a good balance of omega 3 and omega 6