Page 55 - POSTER FYP MAC-OGOS 2025
P. 55
NURUL FATIN INSYIRAH WAN NURUL HUSNA
BINTI MOHD SAIFULLIZAM BINTI WAN NORDIN K242/56
SELECTION OF ROBOT USING FUZZY AHP
ABSTRACT
Selecting the most suitable robot for industrial application is a complex multi-criteria decision-making (MCDM) problem that involves qualitative and
quantitative elements. This research utilized Fuzzy Analytic Hierarchy Process (FAHP) to handle uncertain ties and subjectivity in decision-making. This
method efficiently manages imprecise judgments and emphasizes key selection criteria by integrating fuzzy logic with the traditional AHP framework. In this
research, the criteria and alternatives for the robot selection were adopted from previous research. This research develops a hierarchical model, gathers
committee evaluations, and utilizes FAHP to calculate the weight of criteria and rank alternatives. It followed a structured nine-step procedure that includes
fuzzy pairwise comparisons, geometric mean computation, relative fuzzy weight derivation, defuzzification, and normalization. A case study illustrates how
the proposed method is applicable in real-world industrial situations. FAHP improves the accuracy of decisions by reducing human bias and uncertainty. The
final rankings provide a clear overview of the best choice of the robot based on the chosen criteria. This method helps industries make informed choices,
enhance performance, and lower operational risks.
PROBLEM STATEMENT OBJECTIVES
Traditional multi-criteria decision-making (MCDM) methods that To apply Fuzzy Analytical Hierarchy Process (FAHP) in the selection of
including AHP are often used to solve this problem but it often lead to robot.
inconsistent results. To identify the weight for each criteria.
No uniform methodologies to integrate fuzzy logic with AHP methodology To rank the best criteria and robot using Fuzzy AHP
specifically to the field of robotics.
METHODOLOGY & IMPLEMENTATION
Adoption of data Pairwise Check Calculation Calculation of Calculation Deffuzification
from previous comparisons Consistency of average geometric of Fuzzy and Ranking
research Ratio mean Weight Normalization
RESULTS & DISCUSSION
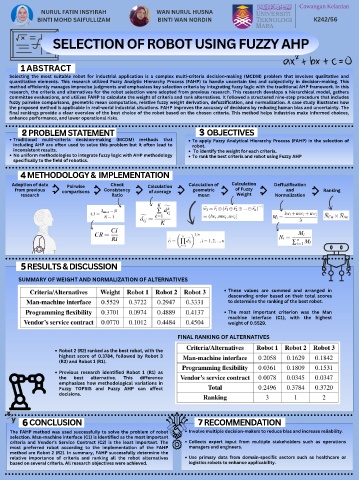
SUMMARY OF WEIGHT AND NORMALIZATION OF ALTERNATIVES
These values are summed and arranged in
descending order based on their total scores
to determine the ranking of the best robot.
The most important criterion was the Man
machine interface (C1), with the highest
weight of 0.5529.
FINAL RANKING OF ALTERNATIVES
Robot 2 (R2) ranked as the best robot, with the
highest score of 0.3784, followed by Robot 3
(R3) and Robot 1 (R1).
Previous research identified Robot 1 (R1) as
the best alternative. This difference
emphasizes how methodological variations in
Fuzzy TOPSIS and Fuzzy AHP can affect
decisions.
CONCLUSION RECOMMENDATION
The FAHP method was used successfully to solve the problem of robot Involve multiple decision-makers to reduce bias and increase reliability.
selection. Man-machine interface (C1) is identified as the most important
criteria and Vendor’s Service Contract (C2) is the least important. The Collects expert input from multiple stakeholders such as operations
most preferred robot according to the implementation of the FAHP managers and engineers.
method are Robot 2 (R2). In summary, FAHP successfully determine the
relative importance of criteria and ranking all the robot alternatives Use primary data from domain-specific sectors such as healthcare or
based on several criteria. All research objectives were achieved. logistics robots to enhance applicability.