Page 276 - Operations Strategy
P. 276
dEvEloPIng oPERATIons CAPAbIlITIEs 251
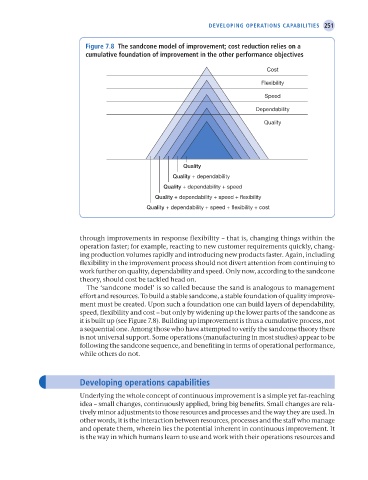
Figure 7.8 the sandcone model of improvement; cost reduction relies on a
cumulative foundation of improvement in the other performance objectives
Cost
Flexibility
Speed
Dependability
Quality
Quality
Quality + dependability
Quality + dependability + speed
Quality + dependability + speed + flexibility
Quality + dependability + speed + flexibility + cost
through improvements in response flexibility – that is, changing things within the
operation faster; for example, reacting to new customer requirements quickly, chang-
ing production volumes rapidly and introducing new products faster. Again, including
flexibility in the improvement process should not divert attention from continuing to
work further on quality, dependability and speed. Only now, according to the sandcone
theory, should cost be tackled head on.
The ‘sandcone model’ is so called because the sand is analogous to management
effort and resources. To build a stable sandcone, a stable foundation of quality improve-
ment must be created. Upon such a foundation one can build layers of dependability,
speed, flexibility and cost – but only by widening up the lower parts of the sandcone as
it is built up (see Figure 7.8). Building up improvement is thus a cumulative process, not
a sequential one. Among those who have attempted to verify the sandcone theory there
is not universal support. Some operations (manufacturing in most studies) appear to be
following the sandcone sequence, and benefiting in terms of operational performance,
while others do not.
Developing operations capabilities
Underlying the whole concept of continuous improvement is a simple yet far-reaching
idea – small changes, continuously applied, bring big benefits. Small changes are rela-
tively minor adjustments to those resources and processes and the way they are used. In
other words, it is the interaction between resources, processes and the staff who manage
and operate them, wherein lies the potential inherent in continuous improvement. It
is the way in which humans learn to use and work with their operations resources and
M07 Operations Strategy 62492.indd 251 02/03/2017 13:06