Page 88 - parasitology for medical and clinical laboratoryprofessionals
P. 88
68 CHAPTER 3
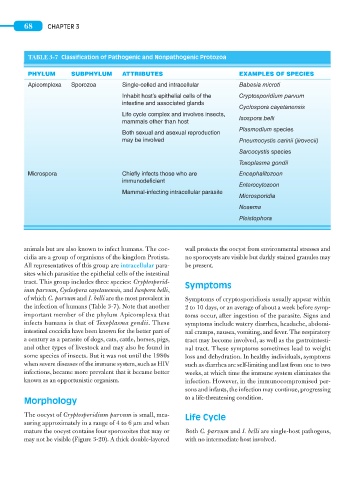
TABLE 3-7 Classification of Pathogenic and Nonpathogenic Protozoa
PHYLUM SUBPHYLUM ATTRIBUTES EXAMPLES OF SPECIES
Apicomplexa Sporozoa Single-celled and intracellular Babesia microti
Inhabit host’s epithelial cells of the Cryptosporidium parvum
intestine and associated glands
Cyclospora cayetanensis
Life cycle complex and involves insects,
mammals other than host Isospora belli
Plasmodium species
Both sexual and asexual reproduction
may be involved Pneumocystis carinii (jirovecii)
Sarcocystis species
Toxoplasma gondii
Microspora Chiefly infects those who are Encephalitozoon
immunodeficient
Enterocytozoon
Mammal-infecting intracellular parasite
Microsporidia
Nosema
Pleistophora
animals but are also known to infect humans. The coc- wall protects the oocyst from environmental stresses and
cidia are a group of organisms of the kingdom Protista. no sporocysts are visible but darkly stained granules may
All representatives of this group are intracellular para- be present.
sites which parasitize the epithelial cells of the intestinal
tract. This group includes three species: Cryptosporid- Symptoms
ium parvum, Cyclospora cayetanensis, and Isospora belli,
of which C. parvum and I. belli are the most prevalent in Symptoms of cryptosporidiosis usually appear within
the infection of humans (Table 3-7). Note that another 2 to 10 days, or an average of about a week before symp-
important member of the phylum Apicomplexa that toms occur, after ingestion of the parasite. Signs and
infects humans is that of Toxoplasma gondii. These symptoms include watery diarrhea, headache, abdomi-
intestinal coccidia have been known for the better part of nal cramps, nausea, vomiting, and fever. The respiratory
a century as a parasite of dogs, cats, cattle, horses, pigs, tract may become involved, as well as the gastrointesti-
and other types of livestock and may also be found in nal tract. These symptoms sometimes lead to weight
some species of insects. But it was not until the 1980s loss and dehydration. In healthy individuals, symptoms
when severe diseases of the immune system, such as HIV such as diarrhea are self-limiting and last from one to two
infections, became more prevalent that it became better weeks, at which time the immune system eliminates the
known as an opportunistic organism. infection. However, in the immunocompromised per-
sons and infants, the infection may continue, progressing
Morphology to a life-threatening condition.
The oocyst of Cryptosporidium parvum is small, mea- Life Cycle
suring approximately in a range of 4 to 6 μm and when
mature the oocyst contains four sporozoites that may or Both C. parvum and I. belli are single-host pathogens,
may not be visible (Figure 3-20). A thick double-layered with no intermediate host involved.