Page 495 - Microeconomics, Fourth Edition
P. 495
c11monopolyandmonopsony.qxd 7/14/10 7:58 PM Page 469
11.5 THE WELFARE ECONOMICS OF MONOPOLY 469
In Chapter 10 we showed that a perfectly competitive equilibrium maximizes social 11.5
welfare (net economic benefit). We also showed that departures from perfectly com- THE WELFARE
petitive equilibrium create deadweight losses. As we will see, the monopoly equilib-
rium does not, in general, correspond to the perfectly competitive equilibrium. For ECONOMICS
that reason, the monopoly equilibrium entails a deadweight loss as well. OF MONOPOLY
THE MONOPOLY EQUILIBRIUM DIFFERS FROM
THE PERFECTLY COMPETITIVE EQUILIBRIUM
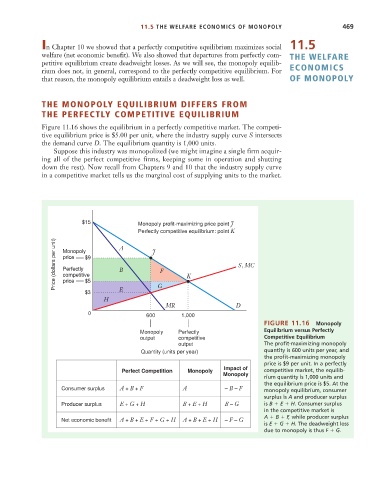
Figure 11.16 shows the equilibrium in a perfectly competitive market. The competi-
tive equilibrium price is $5.00 per unit, where the industry supply curve S intersects
the demand curve D. The equilibrium quantity is 1,000 units.
Suppose this industry was monopolized (we might imagine a single firm acquir-
ing all of the perfect competitive firms, keeping some in operation and shutting
down the rest). Now recall from Chapters 9 and 10 that the industry supply curve
in a competitive market tells us the marginal cost of supplying units to the market.
$15 Monopoly profit-maximizing price point J
Perfectly competitive equilibrium: point K
Price (dollars per unit) Monopoly $9 A J F K S, MC
price
Perfectly
B
competitive
$5
price
$3 E G
H
MR D
0 600 1,000
FIGURE 11.16 Monopoly
Monopoly Perfectly Equilibrium versus Perfectly
output competitive Competitive Equilibrium
output The profit-maximizing monopoly
Quantity (units per year) quantity is 600 units per year, and
the profit-maximizing monopoly
price is $9 per unit. In a perfectly
Impact of
Perfect Competition Monopoly competitive market, the equilib-
Monopoly
rium quantity is 1,000 units and
the equilibrium price is $5. At the
Consumer surplus A + B + F A – B – F monopoly equilibrium, consumer
surplus is A and producer surplus
Producer surplus E + G + H B + E + H B – G is B E H. Consumer surplus
in the competitive market is
Net economic benefit A + B + E + F + G + H A + B + E + H – F – G A B F, while producer surplus
is E G H. The deadweight loss
due to monopoly is thus F G.