Page 223 - Economics
P. 223
CONFIRMING PAGES
PART THREE
194
Macroeconomic Models and Fiscal Policy
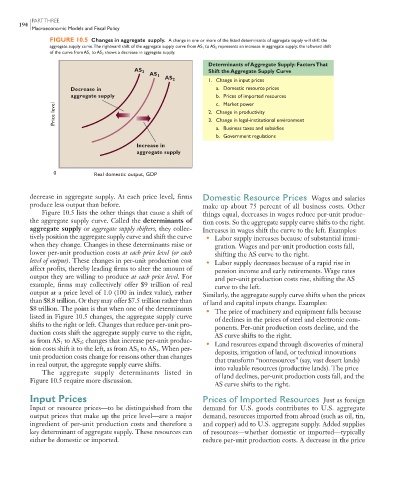
FIGURE 10.5 Changes in aggregate supply. A change in one or more of the listed determinants of aggregate supply will shift the
aggregate supply curve. The rightward shift of the aggregate supply curve from AS 1 to AS 2 represents an increase in aggregate supply; the leftward shift
of the curve from AS 1 to AS 3 shows a decrease in aggregate supply.
Determinants of Aggregate Supply: Factors That
AS 3 Shift the Aggregate Supply Curve
AS 1
AS 2
1. Change in input prices
Decrease in a. Domestic resource prices
aggregate supply b. Prices of imported resources
Price level 2. Change in productivity
c.
Market power
3. Change in legal-institutional environment
a. Business taxes and subsidies
b. Government regulations
Increase in
aggregate supply
0 Real domestic output, GDP
decrease in aggregate supply. At each price level, firms Domestic Resource Prices Wages and salaries
produce less output than before. make up about 75 percent of all business costs. Other
Figure 10.5 lists the other things that cause a shift of things equal, decreases in wages reduce per-unit produc-
the aggregate supply curve. Called the determinants of tion costs. So the aggregate supply curve shifts to the right.
aggregate supply or aggregate supply shifters , they collec- Increases in wages shift the curve to the left. Examples:
tively position the aggregate supply curve and shift the curve • Labor supply increases because of substantial immi-
when they change. Changes in these determinants raise or gration. Wages and per-unit production costs fall,
lower per-unit production costs at each price level (or each shifting the AS curve to the right.
level of output) . These changes in per-unit production cost • Labor supply decreases because of a rapid rise in
affect profits, thereby leading firms to alter the amount of pension income and early retirements. Wage rates
output they are willing to produce at each price level . For and per-unit production costs rise, shifting the AS
example, firms may collectively offer $9 trillion of real curve to the left.
output at a price level of 1.0 (100 in index value), rather Similarly, the aggregate supply curve shifts when the prices
than $8.8 trillion. Or they may offer $7.5 trillion rather than of land and capital inputs change. Examples:
$8 trillion. The point is that when one of the determinants • The price of machinery and equipment falls because
listed in Figure 10.5 changes, the aggregate supply curve of declines in the prices of steel and electronic com-
shifts to the right or left. Changes that reduce per-unit pro- ponents. Per-unit production costs decline, and the
duction costs shift the aggregate supply curve to the right, AS curve shifts to the right.
as from AS to AS ; changes that increase per-unit produc- • Land resources expand through discoveries of mineral
2
1
tion costs shift it to the left, as from AS to AS . When per- deposits, irrigation of land, or technical innovations
1
3
unit production costs change for reasons other than changes that transform “nonresources” (say, vast desert lands)
in real output, the aggregate supply curve shifts. into valuable resources (productive lands). The price
The aggregate supply determinants listed in of land declines, per-unit production costs fall, and the
Figure 10.5 require more discussion.
AS curve shifts to the right.
Input Prices Prices of Imported Resources Just as foreign
Input or resource prices—to be distinguished from the demand for U.S. goods contributes to U.S. aggregate
output prices that make up the price level—are a major demand, resources imported from abroad (such as oil, tin,
ingredient of per-unit production costs and therefore a and copper) add to U.S. aggregate supply. Added supplies
key determinant of aggregate supply. These resources can of resources—whether domestic or imported—typically
either be domestic or imported. reduce per-unit production costs. A decrease in the price
8/21/06 4:51:09 PM
mcc26632_ch10_187-207.indd 194 8/21/06 4:51:09 PM
mcc26632_ch10_187-207.indd 194