Page 569 - Basic College Mathematics with Early Integers
P. 569
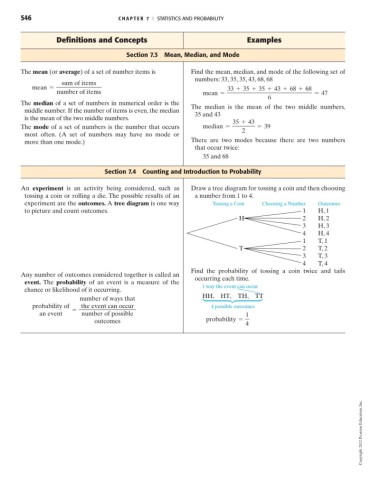
546 C HAPTE R 7 I STATISTICS AND PROBABILITY
Definitions and Concepts Examples
Section 7.3 Mean, Median, and Mode
The mean (or average) of a set of number items is Find the mean, median, and mode of the following set of
numbers: 33, 35, 35, 43, 68, 68
sum of items
mean = 33 + 35 + 35 + 43 + 68 + 68
number of items mean = = 47
6
The median of a set of numbers in numerical order is the
The median is the mean of the two middle numbers,
middle number. If the number of items is even, the median
35 and 43
is the mean of the two middle numbers.
35 + 43
The mode of a set of numbers is the number that occurs median = = 39
2
most often. (A set of numbers may have no mode or
more than one mode.) There are two modes because there are two numbers
that occur twice:
35 and 68
Section 7.4 Counting and Introduction to Probability
An experiment is an activity being considered, such as Draw a tree diagram for tossing a coin and then choosing
tossing a coin or rolling a die. The possible results of an a number from 1 to 4.
experiment are the outcomes. A tree diagram is one way Tossing a Coin Choosing a Number Outcomes
to picture and count outcomes. 1 H, 1
H 2 H, 2
3 H, 3
4 H, 4
1 T, 1
T 2 T, 2
3 T, 3
4 T, 4
Find the probability of tossing a coin twice and tails
Any number of outcomes considered together is called an
occurring each time.
event. The probability of an event is a measure of the
1 way the event can occur
chance or likelihood of it occurring.
HH, HT, TH, TT
number of ways that w
probability of the event can occur 4 possible outcomes
=
an event number of possible 1
outcomes probability =
4
Copyright 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.