Page 731 - Basic Electrical Engineering
P. 731
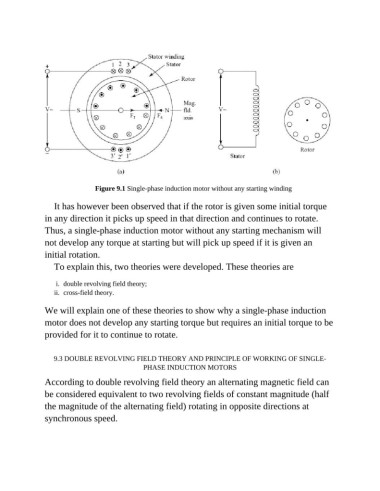
Figure 9.1 Single-phase induction motor without any starting winding
It has however been observed that if the rotor is given some initial torque
in any direction it picks up speed in that direction and continues to rotate.
Thus, a single-phase induction motor without any starting mechanism will
not develop any torque at starting but will pick up speed if it is given an
initial rotation.
To explain this, two theories were developed. These theories are
i. double revolving field theory;
ii. cross-field theory.
We will explain one of these theories to show why a single-phase induction
motor does not develop any starting torque but requires an initial torque to be
provided for it to continue to rotate.
9.3 DOUBLE REVOLVING FIELD THEORY AND PRINCIPLE OF WORKING OF SINGLE-
PHASE INDUCTION MOTORS
According to double revolving field theory an alternating magnetic field can
be considered equivalent to two revolving fields of constant magnitude (half
the magnitude of the alternating field) rotating in opposite directions at
synchronous speed.