Page 732 - Basic Electrical Engineering
P. 732
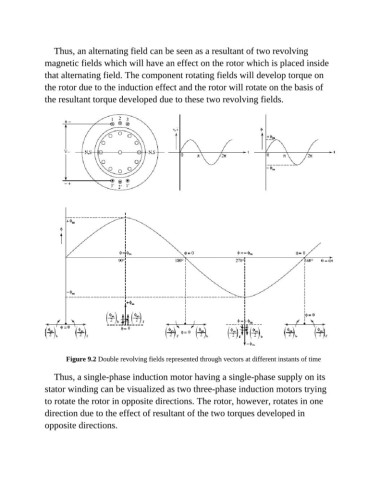
Thus, an alternating field can be seen as a resultant of two revolving
magnetic fields which will have an effect on the rotor which is placed inside
that alternating field. The component rotating fields will develop torque on
the rotor due to the induction effect and the rotor will rotate on the basis of
the resultant torque developed due to these two revolving fields.
Figure 9.2 Double revolving fields represented through vectors at different instants of time
Thus, a single-phase induction motor having a single-phase supply on its
stator winding can be visualized as two three-phase induction motors trying
to rotate the rotor in opposite directions. The rotor, however, rotates in one
direction due to the effect of resultant of the two torques developed in
opposite directions.