Page 83 - Fiber Optic Communications Fund
P. 83
64 Fiber Optic Communications
2
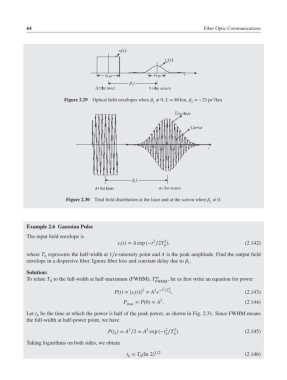
Figure 2.29 Optical field envelopes when ≠ 0. L = 80 km, =−21 ps /km.
2
2
Figure 2.30 Total field distribution at the laser and at the screen when ≠ 0.
2
Example 2.6 Gaussian Pulse
The input field envelope is
2
2
s (t)= A exp (−t ∕2T ), (2.142)
i
0
where T represents the half-width at 1∕e-intensity point and A is the peak amplitude. Find the output field
0
envelope in a dispersive fiber. Ignore fiber loss and constant delay due to .
1
Solution:
To relate T to the full-width at half-maximum (FWHM), T in , let us first write an equation for power
0
FWHM
2 −t ∕T
2
P(t)= |s (t)| = A e 2 2 0 , (2.143)
i
2
P = P(0)= A . (2.144)
max
Let t be the time at which the power is half of the peak power, as shown in Fig. 2.31. Since FWHM means
h
the full-width at half-power point, we have
2
2
2
2
P(t )= A ∕2 = A exp (−t ∕T ). (2.145)
h h 0
Taking logarithms on both sides, we obtain
t = T (ln 2) 1∕2 (2.146)
0
h