Page 3 - FINAL CFA II SLIDES JUNE 2019 DAY 10
P. 3
LOS 37.a: Explain expected exposure, the loss READING 37: CREDIT ANALYSIS MODELS
given default (LGD), the probability of default
(PD), and the credit valuation adjustment (CVA).
MODULE 37.1: CREDIT RISK MEASURES
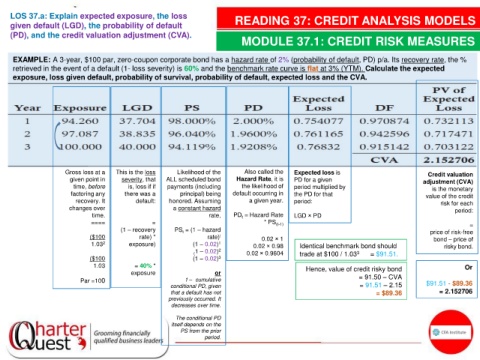
EXAMPLE: A 3-year, $100 par, zero-coupon corporate bond has a hazard rate of 2% (probability of default, PD) p/a. Its recovery rate, the %
retrieved in the event of a default (1- loss severity) is 60% and the benchmark rate curve is flat at 3% (YTM). Calculate the expected
exposure, loss given default, probability of survival, probability of default, expected loss and the CVA.
Gross loss at a This is the loss Likelihood of the Also called the Expected loss is Credit valuation
given point in severity, that ALL scheduled bond Hazard Rate, it is PD for a given adjustment (CVA)
time, before is, loss if if payments (including the likelihood of period multiplied by is the monetary
factoring any there was a principal) being default occurring in the PD for that value of the credit
recovery. It default: honored. Assuming a given year. period: risk for each
changes over a constant hazard period:
time. rate, PD = Hazard Rate LGD × PD
t
==== = * PS (t-1) =
(1 – recovery PS = (1 – hazard price of risk-free
t
($100 rate) * rate) t 0.02 × 1 bond – price of
1.03 2 exposure) (1 – 0.02) 1 0.02 × 0.98 Identical benchmark bond should risky bond.
1 – 0.02) 2
( 0.02 × 0.9604 trade at $100 / 1.03 3 = $91.51.
($100 (1 – 0.02) 3
1.03 = 40% * Hence, value of credit risky bond Or
exposure or
Par =100 1 – cumulative = 91.50 – CVA $91.51 - $89.36
conditional PD, given = 91.51 – 2.15
that a default has not = $89.36 = 2.152706
previously occurred. It
decreases over time.
The conditional PD
itself depends on the
PS from the prior
period.