Page 116 - phytochemistry I - PharmD Clinical
P. 116
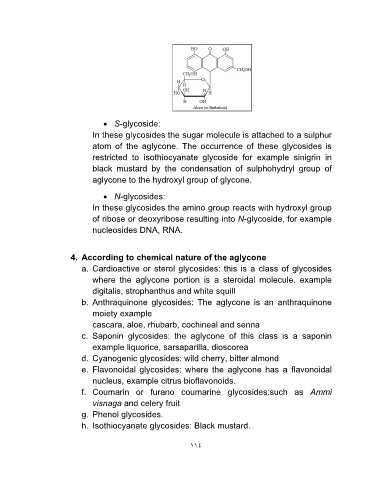
• S-glycoside:
In these glycosides the sugar molecule is attached to a sulphur
atom of the aglycone. The occurrence of these glycosides is
restricted to isothiocyanate glycoside for example sinigrin in
black mustard by the condensation of sulphohydryl group of
aglycone to the hydroxyl group of glycone.
• N-glycosides:
In these glycosides the amino group reacts with hydroxyl group
of ribose or deoxyribose resulting into N-glycoside, for example
nucleosides DNA, RNA.
4. According to chemical nature of the aglycone
a. Cardioactive or sterol glycosides: this is a class of glycosides
where the aglycone portion is a steroidal molecule. example
digitalis, strophanthus and white squill
b. Anthraquinone glycosides: The aglycone is an anthraquinone
moiety example
cascara, aloe, rhubarb, cochineal and senna
c. Saponin glycosides: the aglycone of this class is a saponin
example liquorice, sarsaparilla, dioscorea
d. Cyanogenic glycosides: wild cherry, bitter almond
e. Flavonoidal glycosides: where the aglycone has a flavonoidal
nucleus, example citrus bioflavonoids.
f. Coumarin or furano coumarine glycosides:such as Ammi
visnaga and celery fruit
g. Phenol glycosides.
h. Isothiocyanate glycosides: Black mustard.
۱۱٤