Page 365 - FUNDAMENTALS OF COMPUTER
P. 365
NPP
NPP Memory 365
cessor 8086 has 16 data lines. Therefore a 16 bit {~Q> H$m S>mQ>m ~g h¡ AWm©V² `h EH$ ~ma _| 16- {~Q> n‹T>
word can be read or written at a time. There- `m {bI gH$Vm h¡Ÿ& AV… BgH$s J{V Á`mXm h¡Ÿ& IO,
fore program execution speed is higher. The _o_moar, CPU, ES´>og ~g VWm S>oQ>m ~g H$s pñW{V H$mo
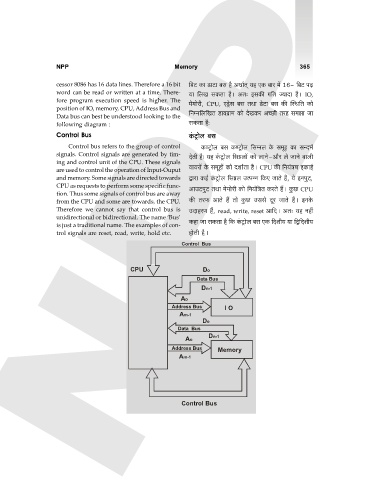
position of IO, memory, CPU, Address Bus and
Data bus can best be understood looking to the {ZåZ{b{IV S>m`J«m_ H$mo XoIH$a AÀN>r Vah g_Pm Om
following diagram : gH$Vm h¡:
Control Bus H§$Q´>mob ~g
Control bus refers to the group of control H$ÊQ´>mob ~g H$ÊQ´>mob {g½Zb Ho$ g‘yh H$m gÝX^©
signals. Control signals are generated by tim- XoVr h¡& `h H§$Q´>mob {g¾bm| H$mo bmZo-Am¡a bo OmZo dmbr
ing and control unit of the CPU. These signals
are used to control the operation of Input-Ouput dm`am| Ho$ g_yhm| H$mo Xem©Vm h¡Ÿ& CPU H$s {Z`§ÌU BH$mB©
and memory. Some signals are directed towards Ûmam H$B© H§$Q´>mob {g¾b CËnÝZ {H$E OmVo h¢, `o BZnwQ,>
CPU as requests to perform some specific func- AmCQ>nwQ> VWm _o_moar H$mo {Z`§{ÌV H$aVo h¢Ÿ& Hw$N> CPU
tion. Thus some signals of control bus are away
from the CPU and some are towards, the CPU. H$s Va\$ AmVo h¢ Vmo Hw$N> Cggo Xya OmVo h¢Ÿ& BZHo$
Therefore we cannot say that control bus is CXmhaU h¢, read, write, reset Am{XŸ& AV… `h Zht
unidirectional or bidirectional. The name ‘Bus’
is just a traditional name. The examples of con- H$hm Om gH$Vm h¡ {H$ H§$Q´>mob ~g EH$ {Xer` `m {Û{Xer`
trol signals are reset, read, write, hold etc. hmoVr h¡Ÿ&
Control Bus
CPU Do
Data Bus
Dn-1
Ao
Address Bus I O
Am-1
Do
Data Bus
Dn-1
Ao
Address Bus Memory
Am-1
Control Bus