Page 385 - FUNDAMENTALS OF COMPUTER
P. 385
NPP
NPP CPU Architecture, Addressing Modes and Data Transfer Schemes 385
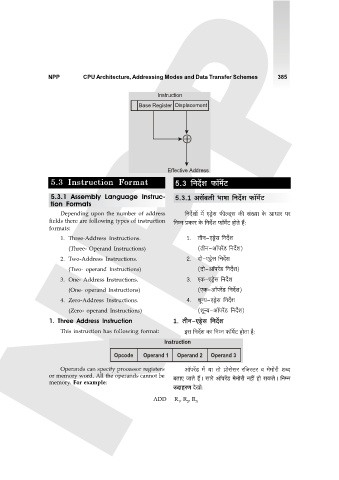
Instruction
Base Register Displacement
⊕
Effective Address
5.3 Instruction Format 5.3 {ZX}e \$m°_}Q>
5.3.1 Assembly Language Instruc- 5.3.1 Ag|~cr ^mfm {ZX}e \$m°_}Q>
tion Formats
Depending upon the number of address {ZX}em| _| ES´>og \$sëS>²g H$s g§»`m Ho$ AmYma na
fields there are following types of instruction {ZåZ àH$ma Ho$ {ZX}e \$m°_}Q> hmoVo h¢:
formats:
1. Three-Address Instructions. 1. VrZ-ES´>og {ZX}e
(Three- Operand Instructions) (VrZ-Am°na|S> {ZX}e)
2. Two-Address Instructions. 2. Xmo-ES´>og {ZX}e
(Two- operand Instructions) (Xmo-Am°na|S> {ZX}e)
3. One- Address Instructions. 3. EH$-ES´>og {ZX}e
(One- operand Instructions) (EH$-Am°na|S> {ZX}e)
4. Zero-Address Instructions. 4. eyÝ`-ES´>og {ZX}e
(Zero- operand Instructions) (eyÝ`-Am°na|S> {ZX}e)
1. Three Address Instruction 1. VrZ-ES´>og {ZX}e
This instruction has following format: Bg {ZX}e H$m {ZåZ \$m°_}Q> hmoVm h¡:
Instruction
Opcode Operand 1 Operand 2 Operand 3
Operands can specify processor registers Am°na|S> _| `m Vmo àmogoga a{OñQ>a d _o_moar eãX
or memory word. All the operands cannot be ~VmE OmVo h¢Ÿ& gmao Am°na|S> _o_moar Zht hmo gH$VoŸ& {ZåZ
memory. For example:
CXmhaU XoImo:
ADD R , R , R 3
2
1