Page 18 - PR 2014 2016 03 Applications of Ionizing Radiations
P. 18
60 Application of Ionizing Radiations | Progress Report
ed area of 2.7 million hectares, but the coconut sterilization. Enzymatic and soil degradation
husk fiber has not been used much for industri- were not negatively affected by radiation pro-
al applications. Moreover, when considering an cessing. Even though fiber incorporation to
application in the medical field, it is necessary the polymer blend slightly reduced degrada-
that the products are sterilized and, ionizing tion process, composites continued degrading
radiation is widely used to sterilize medical through time. Artifacts produced by means of
and surgical devices. In this research, blends the materials studied here can be radiation
and composites based on two commercial processed with doses up to 100 kGy without
polymers: poly (ε-caprolactone), PCL, and poly prejudice of their biodegradability. Cytotox-
(lactic acid), PLLA, and coconut fiber have been icity In vitro results of lixiviate indicated that
studied. Samples were irradiated with gam- composites did no present IC50, so the quantity
ma rays from Co source and, electron beam of substances released that would cause cell
60
from Dynamitron Accelerator, with radiation death was not significant.
doses ranging from 10 kGy up to 1 MGy. The
non-irradiated and irradiated samples were
studied using several analytical techniques
and characterization assays that allowed un-
derstanding their properties in order to enable
their application as precursors for medical and
surgical devices. Thermal processing used to
obtain composites and previous acetylation by
chemical treatment of coconut fibers contrib-
uted to the bioburden reduction. Furthermore,
reducing initial bioburden it was possible to
diminish radiation doses needed to perform
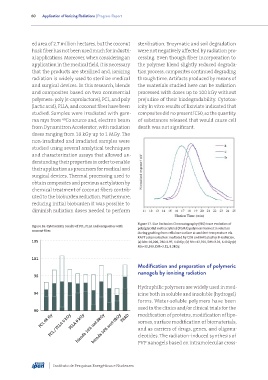
Figure 27. Size Exclusion Chromatography (SEC) trace evolution of
Figure 26. Cytotoxicity results of PCL, PLLA and composites with poly(glycidyl methacrylate) (PGMA) polymers formed in solution
coconut fiber.
during grafting from cellulose surface at ambient temperature via
RAFT polymerization mediated by CDB and initiated by γ-radiation.
105 (a) Mn=10,200, DM=2.97, 4.4kGy; (b) Mn=12,700, DM=3.26, 6.4kGy;(c)
Mn=35,300, DM=3.52, 8.3kGy.
101
Modification and preparation of polymeric
nanogels by ionizing radiation
98
Hydrophilic polymers are widely used in med-
94 icine both in soluble and insoluble (hydrogel)
forms. Water-soluble polymers have been
used in the clinics and/or clinical trials for the
90 modification of proteins, modification of lipo-
PCL 0k Gy PCL / PLLA 0 kGy PLLA 0 kGy bienda 10% acet 0kGy PEAD somes, surface modification of biomaterials,
bienda 10% unt 0kGy
and as carriers of drugs, genes, and oligonu-
cleotides. The radiation-induced synthesis of
PVP nanogels based on intramolecular cross-
Instituto de Pesquisas Energéticas e Nucleares