Page 72 - manual_V5_11_9_2018_Html5
P. 72
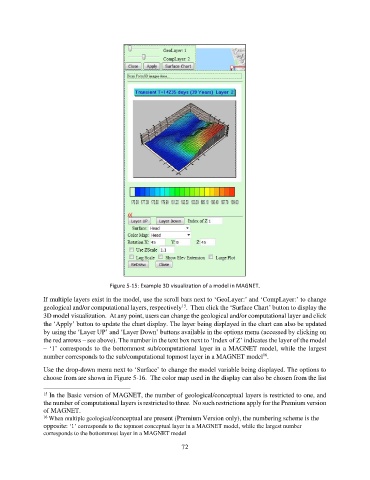
Figure 5-15: Example 3D visualization of a model in MAGNET.
If multiple layers exist in the model, use the scroll bars next to ‘GeoLayer:’ and ‘CompLayer:’ to change
15
geological and/or computational layers, respectively . Then click the ‘Surface Chart’ button to display the
3D model visualization. At any point, users can change the geological and/or computational layer and click
the ‘Apply’ button to update the chart display. The layer being displayed in the chart can also be updated
by using the ‘Layer UP’ and ‘Layer Down’ buttons available in the options menu (accessed by clicking on
the red arrows – see above). The number in the text box next to ‘Index of Z’ indicates the layer of the model
– ‘1’ corresponds to the bottommost sub/computational layer in a MAGNET model, while the largest
16
number corresponds to the sub/computational topmost layer in a MAGNET model .
Use the drop-down menu next to ‘Surface’ to change the model variable being displayed. The options to
choose from are shown in Figure 5-16. The color map used in the display can also be chosen from the list
15 In the Basic version of MAGNET, the number of geological/conceptual layers is restricted to one, and
the number of computational layers is restricted to three. No such restrictions apply for the Premium version
of MAGNET.
16 When multiple geological/conceptual are present (Premium Version only), the numbering scheme is the
opposite: ‘1’ corresponds to the topmost conceptual layer in a MAGNET model, while the largest number
corresponds to the bottommost layer in a MAGNET model
72