Page 10 - sackcasestudy
P. 10
9
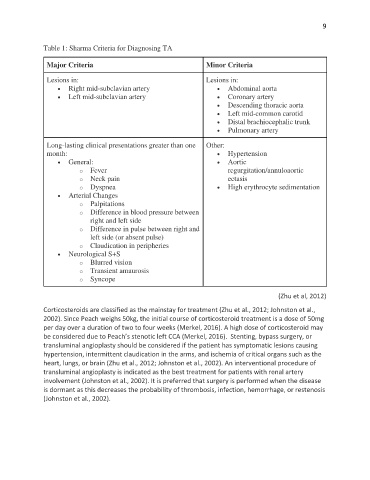
Table 1: Sharma Criteria for Diagnosing TA
Major Criteria Minor Criteria
Lesions in: Lesions in:
• Right mid-subclavian artery • Abdominal aorta
• Left mid-subclavian artery • Coronary artery
• Descending thoracic aorta
• Left mid-common carotid
• Distal brachiocephalic trunk
• Pulmonary artery
Long-lasting clinical presentations greater than one Other:
month: • Hypertension
• General: • Aortic
o Fever regurgitation/annuloaortic
o Neck pain ectasis
o Dyspnea • High erythrocyte sedimentation
• Arterial Changes
o Palpitations
o Difference in blood pressure between
right and left side
o Difference in pulse between right and
left side (or absent pulse)
o Claudication in peripheries
• Neurological S+S
o Blurred vision
o Transient amaurosis
o Syncope
(Zhu et al, 2012)
Corticosteroids are classified as the mainstay for treatment (Zhu et al., 2012; Johnston et al.,
2002). Since Peach weighs 50kg, the initial course of corticosteroid treatment is a dose of 50mg
per day over a duration of two to four weeks (Merkel, 2016). A high dose of corticosteroid may
be considered due to Peach’s stenotic left CCA (Merkel, 2016). Stenting, bypass surgery, or
transluminal angioplasty should be considered if the patient has symptomatic lesions causing
hypertension, intermittent claudication in the arms, and ischemia of critical organs such as the
heart, lungs, or brain (Zhu et al., 2012; Johnston et al., 2002). An interventional procedure of
transluminal angioplasty is indicated as the best treatment for patients with renal artery
involvement (Johnston et al., 2002). It is preferred that surgery is performed when the disease
is dormant as this decreases the probability of thrombosis, infection, hemorrhage, or restenosis
(Johnston et al., 2002).