Page 236 - 00. Complete Version - Progress Report IPEN 2014-2016
P. 236
236 Environmental Science and Technology | Progress Report
lem, researchers of CQMA have performed a Besides the development of characterization
study that aimed to develop and validate a methods, IPEN has also developed advanced
method to identify and quantify persistent processes for safe decomposition of POPs. The
organic pollutants, known as POPs in soil of technology developed at IPEN is applicable to
industrial regions Caieiras and Franco da Ro- intrinsically safe disposal of hazardous organ-
cha municipalities in São Paulo by gas chro- ic wastes, particularly the organochlorides,
matography coupled with Mass Spectrometry whose degradation has presented problems
(GC/MS) and Electron Capture Detector (GC/ when using the most common methods, such
ECD), as it can be observed in the figures 1 and as incineration. The molten salt oxidation is a
2. To ensure reliability of the analysis carried process which promotes a more complete and
out, tests were carried out validation meth- safer decomposition of wastes considered crit-
od. The extraction technique used was QuEC- ical, such as POPs, as can be observed schemat-
hERS, achieving recovery in the range 70 to ically in the figure 3.
120% for most of the compounds, acceptable
for complex matrices. The limits of detection Organochloride compounds can be decom-
and quantification of the method comprises posed in a safe way in the molten salt equip-
the range of 0.0002 and 0.01 µg.g-1, respec- ment because the chlorine present in the
tively. The samples analyzed were contami- wastes reacts with elements present in the
nated by compounds hexachlorobenzene α, α, bath salt, such as sodium, for example, form-
α and α, many of which are above the maxi- ing the sodium chloride which is retained in
mum allowable in accordance with national the salt. It is important to mention that the
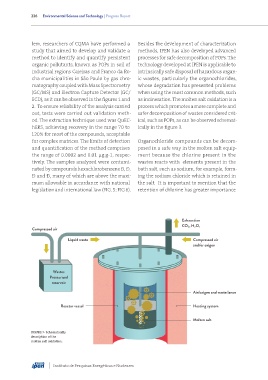
legislation and international law (FIG. 5; FIG 6). retention of chlorine has greater importance
Exhaustion
CO 2, H 2O v
Compressed air
Liquid waste Compressed air
and/or oxigen
Wastes
Pressurized
reservoir
Air/oxigen and waste lance
Reactor vessel Heating system
Molten salt
FIGURE 7- Schematically
description of the
molten salt oxidation.
Instituto de Pesquisas Energéticas e Nucleares