Page 249 - rise 2017
P. 249
show job satisfaction increased when organization given more appreciation towards their staffs.
Furthermore, intrinsic rewards encourage high motivation that leads to satisfaction of employees.
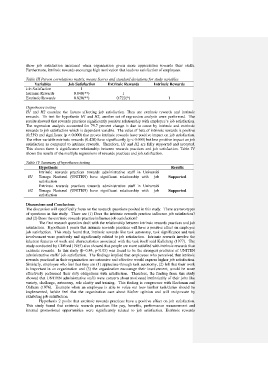
Table III Person correlations matrix, means Scores and standard deviations for study variables
Variables Job Satisfaction Extrinsic Rewards Intrinsic Rewards
Job Satisfaction 1
Intrinsic Rewards 0.840(**) 1
Extrinsic Rewards 0.820(**) 0.722(*) 1
Hypotheses testing
H1 and H2 examine the factors affecting job satisfaction. They are extrinsic rewards and intrinsic
rewards. To test for hypothesis H1 and H2, another set of regression analysis were performed. The
results showed that rewards practices significantly positive relationship with employee’s job satisfaction.
The regression analysis accounted for 79.7 percent change is due to cause by intrinsic and extrinsic
rewards to job satisfaction which is dependent variable. The value of beta of intrinsic rewards is positive
(0.539) and significant (p < 0.000) that proves intrinsic rewards have positive impact on job satisfaction.
The other variable extrinsic rewards (0.420) have significantly (p < 0.000) but less positive impact on job
satisfaction as compared to intrinsic rewards. Therefore, H1 and H2 are fully supported and accepted.
This shows there is significance relationship between rewards practices and job satisfaction. Table IV
shows the results of the multiple regressions of rewards practices and job satisfaction.
Table IV Summary of hypotheses testing
Hypothesis Results
Intrinsic rewards practices towards administrative staff in Universiti
H1 Tenaga Nasional (UNITEN) have significant relationship with job Supported
satisfaction
Extrinsic rewards practices towards administrative staff in Universiti
H2 Tenaga Nasional (UNITEN) have significant relationship with job Supported
satisfaction
Discussions and Conclusions
The discussion will specifically focus on the research questions posited in this study. There are two types
of questions in this study. There are (1) Does the intrinsic rewards practice influence job satisfaction?
and (2) Does the extrinsic rewards practice influence job satisfaction?
The first research question dealt with the relationship between intrinsic rewards practices and job
satisfaction. Hypothesis 1 posits that intrinsic rewards practices will have a positive effect on employee
job satisfaction. This study found that, intrinsic rewards like task autonomy, task significance and task
involvement were positively and significantly related to job satisfaction. Intrinsic rewards involve the
inherent features of work and characteristics associated with the task itself said Kalleberg (1977). The
study conducted by Clifford (1985) also showed that people are more satisfied with intrinsic rewards than
extrinsic rewards. In this study (β=0.84, p<0.05) was found to be the strongest predictor of UNITEN
administrative staffs’ job satisfaction. The findings implied that employees who perceived that intrinsic
rewards practiced in their organization are extensive and effective would express higher job satisfaction.
Similarly, employee who feel that they are (1) appreciate through task autonomy, (2) felt that their work
is important in an organization and (3) the organization encourage their involvement, would be more
effectively performed their duty obligations with satisfaction. Therefore, the finding from this study
showed that UNITEN administrative staffs were concern about motivated intrinsically of their jobs like
variety, challenge, autonomy, role clarity and training. This finding is congruence with Hackman and
Oldham (1976). Example when an employee is able to voice out how his/her task/duties should be
implemented, he/she feel that the organization care about his/her opinion and will reciprocate by
exhibiting job satisfaction.
Hypothesis 2 posits that extrinsic rewards practices have a positive effect on job satisfaction.
This study found that extrinsic rewards practices like pay, benefits, performance measurement and
internal promotional opportunities were significantly related to job satisfaction. Extrinsic rewards