Page 8 - PR 2014 2016 10 Materials and Nanotechnology
P. 8
284 Materials and Nanotechnology | Progress Report
Determinants of corrosion resistance of 4V alloy were these typical of occluded cells,
Ti-6Al-4V alloy dental implants in an in i.e. oxidizing conditions (H O ), high acidity
2
2
vitro model of peri-implant (pH=3), presence of protein and deaeration of
the physiological medium. Our results provide
Titanium (Ti) and its alloys are widely used evidence that titanium corrosion can be trig-
for manufacturing dental implants and or- gered by intense inflammatory conditions.
thopedic prostheses owing to their high bio-
compatibility and corrosion resistance. These Zirconia dental ceramics
favorable properties for in vivo implantation
are due to Ti ability to form a passive oxide Yttria tetragonal zirconia polycrystals (Y-TZP)
film, i.e. TiO , immediately after contact with have been used in dentistry for metal free
2
oxygen. This passive layer is very stable and prosthesis due to esthetics associated with a
adherent to the Ti surface during function high mechanical performance. However, the
in the oral cavity. However, up to 20% of presence of humid environment can cause
individuals with dental implants develop an accelerated tetragonal to monoclinic (t-m)
peri-implantitis; a chronic inflammatory dis- phase transformation and consequent cat-
ease causing loss of jawbone and eventually astrophic failure of this material. This pro-
implant failure and removal. The etiology of cess, known as low temperature degradation
peri-implantitis has not been fully unraveled, (LTD) or aging, has been evaluated in vitro
but has been traditionally considered to be in our laboratory in a hydrothermal pressur-
associated to microbial infection. Recent re- ized reactor at 150°C in order to accelerate
sults from our group, however, have found the crystallite phase transformation kinetics.
that Ti corrosion products are vastly increased The degradation studies have been performed
around diseased implants as compared to in commercial and laboratory synthesized
healthy ones. This observation indicates that dental ceramics.
the micro-environment to which the implant
is exposed during peri-implant inflammation The aim of commercial dental Y-TZP studies
is highly aggressive leading to TiO passive was the determination of speed of the front
2
layer attack. The aim of this work is to sim- of phase transformation zone growth during
ulate peri-implant inflammatory conditions hydrothermal aging, and to correlate with the
in vitro to determine which factors affect biaxial flexural strength. The effect of the asso-
corrosion susceptibility of Ti-6Al-4V dental
implants in phosphate solution. The effect of
hydrogen peroxide (surrogate for reactive oxy-
gen species, ROS, found during inflammation),
albumin (a protein typical of physiological
fluids), deaeration (to simulate reduced pO2
conditions during inflammation), and pH
(3, 4.5 and 7) were investigated. The corro-
sion resistance of Ti-6Al-4V was performed
by electrochemical techniques and surface
characterization after exposure to corrosion
immersion test. The results showed that the
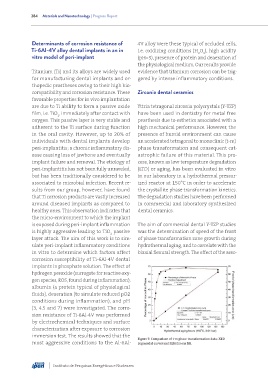
Figure 7: Comparison of t-m phase transformation data: XRD
most aggressive conditions to the Al-6Al- (sigmoidal curve) and SEM (linear fit).
Instituto de Pesquisas Energéticas e Nucleares