Page 1163 - Equine Clinical Medicine, Surgery and Reproduction, 2nd Edition
P. 1163
1138 CHAPTER 11
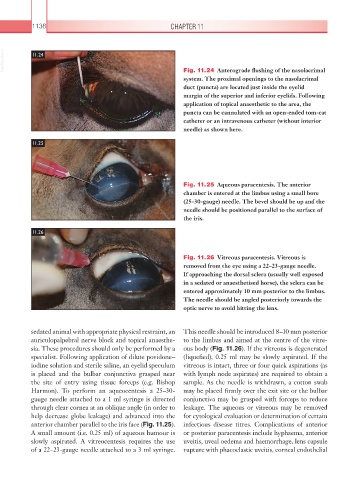
VetBooks.ir 11.24
Fig. 11.24 Anterograde flushing of the nasolacrimal
system. The proximal openings to the nasolacrimal
duct (puncta) are located just inside the eyelid
margin of the superior and inferior eyelids. Following
application of topical anaesthetic to the area, the
puncta can be cannulated with an open-ended tom-cat
catheter or an intravenous catheter (without interior
needle) as shown here.
11.25
Fig. 11.25 Aqueous paracentesis. The anterior
chamber is entered at the limbus using a small bore
(25–30-gauge) needle. The bevel should be up and the
needle should be positioned parallel to the surface of
the iris.
11.26
Fig. 11.26 Vitreous paracentesis. Vitreous is
removed from the eye using a 22–23-gauge needle.
If approaching the dorsal sclera (usually well exposed
in a sedated or anaesthetised horse), the sclera can be
entered approximately 10 mm posterior to the limbus.
The needle should be angled posteriorly towards the
optic nerve to avoid hitting the lens.
sedated animal with appropriate physical restraint, an This needle should be introduced 8–10 mm posterior
auriculopalpebral nerve block and topical anaesthe- to the limbus and aimed at the centre of the vitre-
sia. These procedures should only be performed by a ous body (Fig. 11.26). If the vitreous is degenerated
specialist. Following application of dilute povidone– (liquefied), 0.25 ml may be slowly aspirated. If the
iodine solution and sterile saline, an eyelid speculum vitreous is intact, three or four quick aspirations (as
is placed and the bulbar conjunctiva grasped near with lymph node aspirates) are required to obtain a
the site of entry using tissue forceps (e.g. Bishop sample. As the needle is withdrawn, a cotton swab
Harmon). To perform an aqueocentesis a 25–30- may be placed firmly over the exit site or the bulbar
gauge needle attached to a 1 ml syringe is directed conjunctiva may be grasped with forceps to reduce
through clear cornea at an oblique angle (in order to leakage. The aqueous or vitreous may be removed
help decrease globe leakage) and advanced into the for cytological evaluation or determination of certain
anterior chamber parallel to the iris face (Fig. 11.25). infectious disease titres. Complications of anterior
A small amount (i.e. 0.25 ml) of aqueous humour is or posterior paracentesis include hyphaema, anterior
slowly aspirated. A vitreocentesis requires the use uveitis, uveal oedema and haemorrhage, lens capsule
of a 22–23-gauge needle attached to a 3 ml syringe. rupture with phacoclastic uveitis, corneal endothelial