Page 1334 - Equine Clinical Medicine, Surgery and Reproduction, 2nd Edition
P. 1334
Wound management and infections of synovial structures 1309
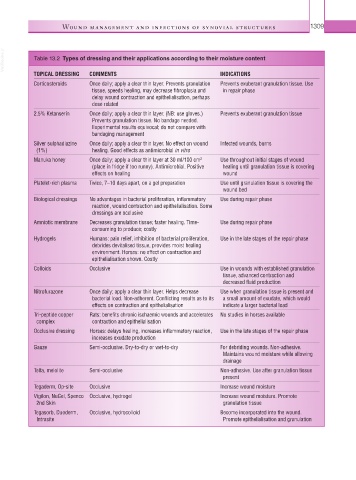
VetBooks.ir Table 13.2 Types of dressing and their applications according to their moisture content
TOPICAL DRESSING COMMENTS INDICATIONS
Corticosteroids Once daily; apply a clear thin layer. Prevents granulation Prevents exuberant granulation tissue. Use
tissue, speeds healing, may decrease fibroplasia and in repair phase
delay wound contraction and epithelialisation, perhaps
dose related
2.5% Ketanserin Once daily; apply a clear thin layer. (NB: use gloves.) Prevents exuberant granulation tissue
Prevents granulation tissue. No bandage needed.
Experimental results equivocal; do not compare with
bandaging management
Silver sulphadiazine Once daily; apply a clear thin layer. No effect on wound Infected wounds, burns
(1%) healing. Good effects as antimicrobial in vitro
Manuka honey Once daily; apply a clear thin layer at 30 ml/100 cm Use throughout initial stages of wound
2
(place in fridge if too runny). Antimicrobial. Positive healing until granulation tissue is covering
effects on healing wound
Platelet-rich plasma Twice, 7–10 days apart, on a gel preparation Use until granulation tissue is covering the
wound bed
Biological dressings No advantages in bacterial proliferation, inflammatory Use during repair phase
reaction, wound contraction and epithelialisation. Some
dressings are occlusive
Amniotic membrane Decreases granulation tissue; faster healing. Time- Use during repair phase
consuming to produce; costly
Hydrogels Humans: pain relief, inhibition of bacterial proliferation, Use in the late stages of the repair phase
debrides devitalised tissue, provides moist healing
environment. Horses: no effect on contraction and
epithelialisation shown. Costly
Colloids Occlusive Use in wounds with established granulation
tissue, advanced contraction and
decreased fluid production
Nitrofurazone Once daily; apply a clear thin layer. Helps decrease Use when granulation tissue is present and
bacterial load. Non-adherent. Conflicting results as to its a small amount of exudate, which would
effects on contraction and epithelialisation indicate a larger bacterial load
Tri-peptide copper Rats: benefits chronic ischaemic wounds and accelerates No studies in horses available
complex contraction and epithelialisation
Occlusive dressing Horses: delays healing, increases inflammatory reaction, Use in the late stages of the repair phase
increases exudate production
Gauze Semi-occlusive. Dry-to-dry or wet-to-dry For debriding wounds. Non-adhesive.
Maintains wound moisture while allowing
drainage
Telfa, melolite Semi-occlusive Non-adhesive. Use after granulation tissue
present
Tegaderm, Op-site Occlusive Increase wound moisture
Vigilon, NuGel, Spenco Occlusive, hydrogel Increase wound moisture. Promote
2nd Skin granulation tissue
Tegasorb, Duoderm, Occlusive, hydrocolloid Become incorporated into the wound.
Intrasite Promote epithelialisation and granulation